Introduction
In 2024, global sales of GLP-1 drugs exceeded $50 billion, confirming the strong growth of the weight-loss drug market. In only the first half of 2025, the global transaction volume in the weight-loss sector has already surpassed $24.675 billion, with increasing capital investment and major companies expanding their involvement.
While multinational corporations continue to invest heavily, the focus is gradually shifting. The weight-loss drug market is moving beyond the GLP-1 toward a phase characterized by multiple mechanisms. Targets such as amylin are drawing increasing attention for their potential to enhance treatment outcomes. Emerging mechanisms like ACSL5 and ActRII indicate that next-generation weight-loss drugs are driving changes in the market structure.
GLP-1 Treatments Shift Toward Multi-Target Approaches
In the field of obesity treatment, the value of targeting GLP-1 has been validated by the global market. However, the limitations of single-target therapies are becoming increasingly evident. Multi-target drugs, with their superior metabolic regulation and combined therapeutic effects, are emerging as a new mainstream in drug development. Dual-target therapies—such as Tirzepatide, HS-20094, and Mazdutide—have demonstrated improved outcomes in both blood glucose control and weight reduction. As a result, the development of GLP-1-based therapies is rapidly shifting toward multi-target approaches.
Mazdutide, developed by Innovent Biologics, is the world’s first and only GCG/GLP-1 dual receptor agonist submitted for regulatory approval for weight loss and blood glucose control. Results from its Phase III clinical trial (GLORY-1) were recently published in full in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). The study showed that Mazdutide led to significant weight loss among Chinese individuals with obesity and demonstrated a favourable safety profile.
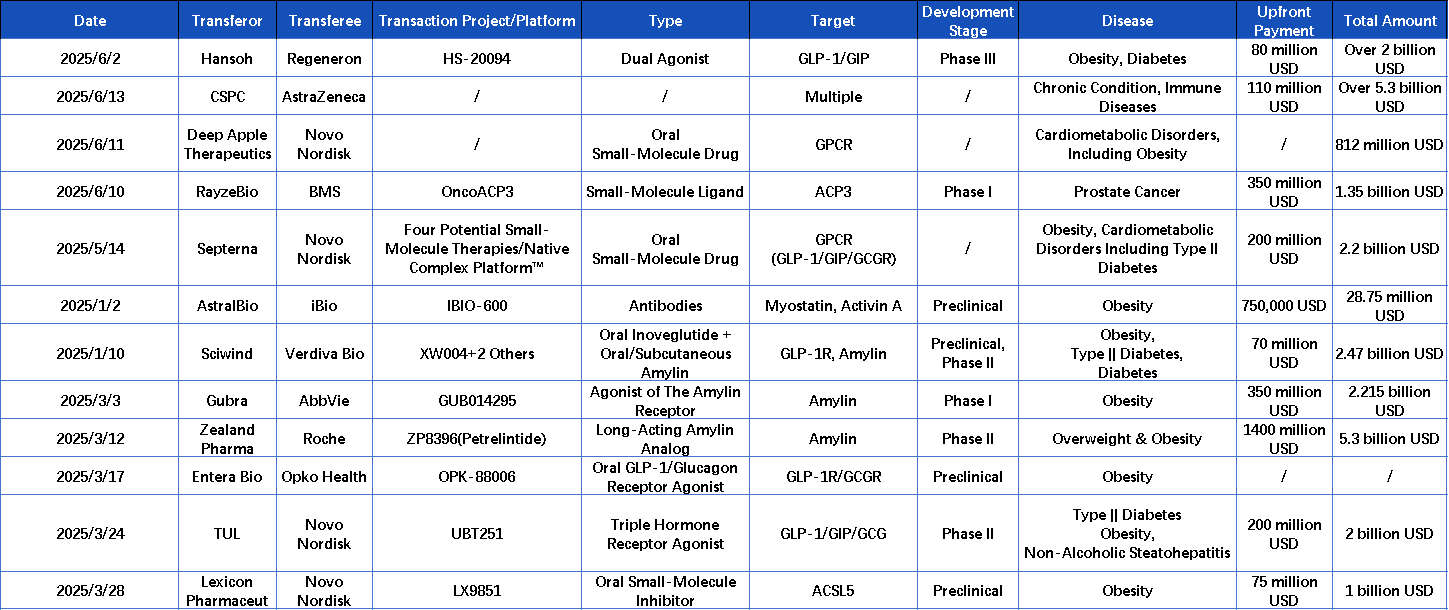
A notable recent development occurred on June 2, when Hansoh Pharma signed a licensing agreement with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Under the agreement, Hansoh granted Regeneron exclusive rights to develop, manufacture, and commercialize HS-20094 globally, excluding mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau. HS-20094 is an investigational GLP-1/GIP receptor agonist that has completed multiple Phase II clinical trials, demonstrating favourable efficacy and safety. It is currently undergoing Phase III clinical trials in China.
These developments reflect a clear shift in the obesity treatment landscape, where innovation is increasingly driven by multi-target strategies. This trend not only highlights the growing demand for more effective and safer therapies but also signals that multi-mechanism approaches are likely to shape the next phase of advancement in metabolic disease treatment.
The Rising Importance of Amylin
From a mechanistic perspective, amylin is co-secreted with insulin by pancreatic β-cells and plays a role in regulating gastric emptying, increasing satiety, and suppressing appetite. It not only offers metabolic benefits such as reducing glucagon levels, improving leptin signaling, and regulating blood glucose but also helps decrease energy intake, making it a natural factor in body weight regulation.
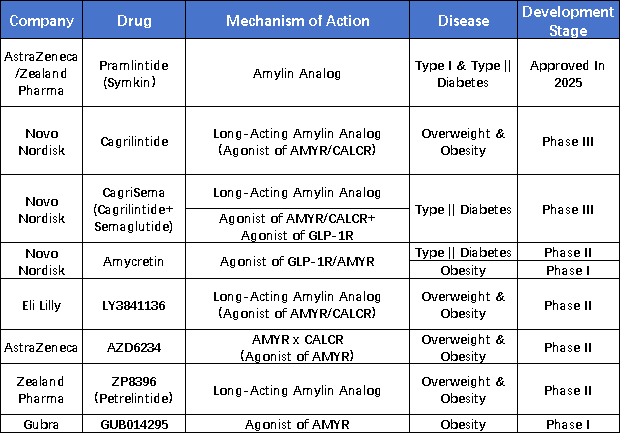
In recent years, amylin therapy has increasingly been recognized by pharmaceutical companies as a new growth driver beyond GLP-1. This trend is also reflected in deal activity: in March of this year, Roche and Zealand reached a collaboration agreement for petrelintide involving a $1.4 billion upfront payment and a total value of $5.3 billion. Early data showed the drug achieved an 8.6% weight loss over four months with lower incidences of nausea. AbbVie also invested $2.2 billion to acquire Danish company Gubra, strengthening its portfolio with the long-acting amylin analog GUB014295. This marks AbbVie’s first entry into the amylin-based weight-loss market.
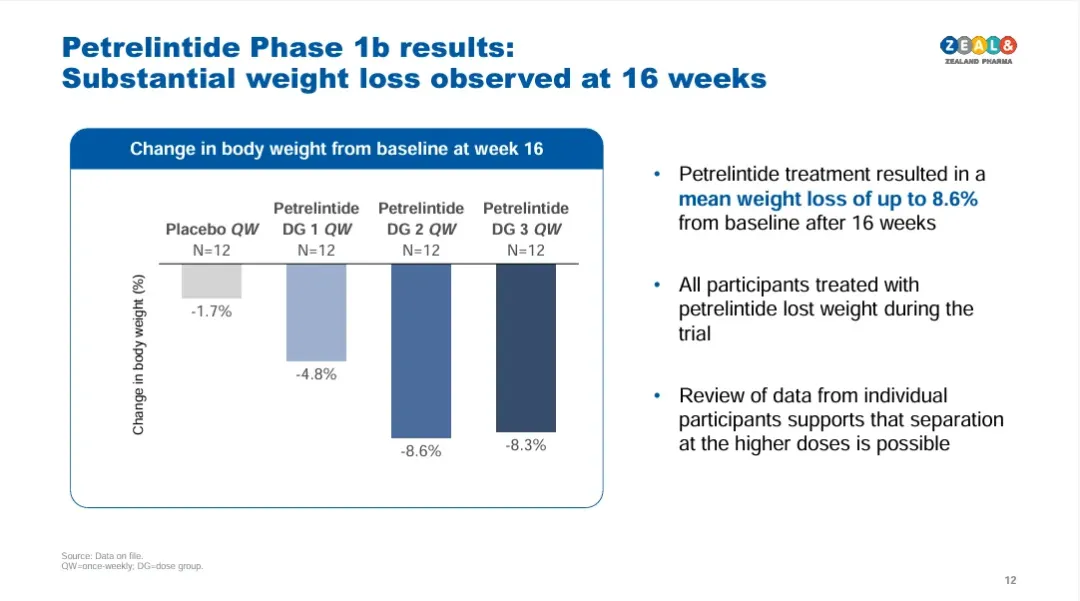
On June 14, Eli Lilly released the latest early trial summary of its experimental amylin-based drug, Eloralintide. The 12-week trial data showed a maximum weight loss of 11.3%, with mild side effects and better tolerability than GLP-1 therapies. Its performance not only surpassed petrelintide, developed jointly by Roche and Zealand, but also sparked widespread industry attention on the amylin target.
In addition, AstraZeneca is also advancing the early clinical development of its amylin program.
Novo Nordisk’s CagriSema, a combination of semaglutide and cagrilintide, has further advanced the synergistic potential of GLP-1 and amylin. In Phase III trials, it achieved a weight loss rate of 22.7%. Although it did not meet the predefined primary endpoint, the efficacy was comparable to that of tirzepatide, highlighting the significant value of amylin as a complementary target.
Emerging Therapeutic Targets
ACSL5
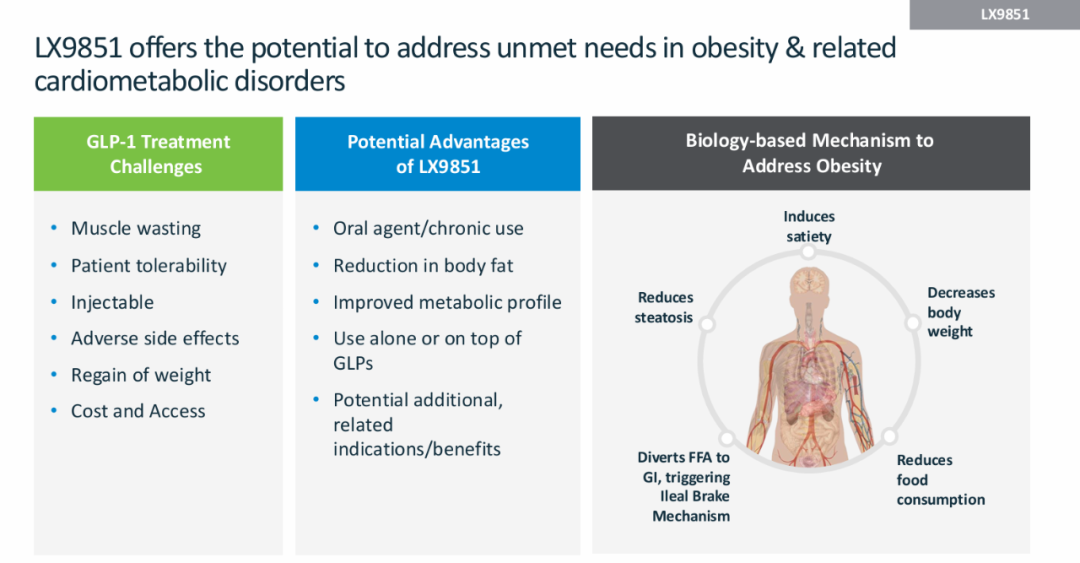
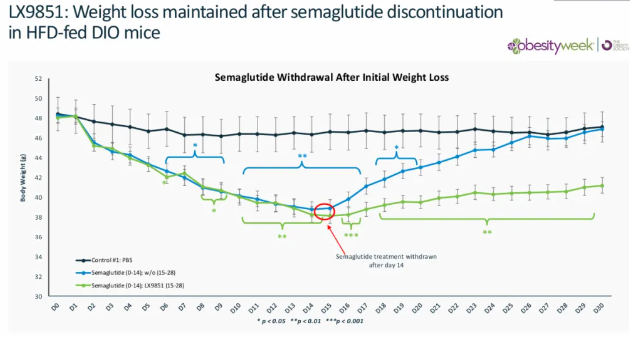
ACSL5 plays a critical role in fat accumulation and energy balance metabolic pathways. In November 2024, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals presented preclinical in vivo data for LX9851, showing that the candidate drug significantly reduced food intake, fat mass, and overall body weight in mice. Notably, LX9851 also helped mitigate weight regain after discontinuation of semaglutide treatment and demonstrated a positive effect on hepatic steatosis.
As the only ACSL5-targeting drug currently in development, LX9851 has shown promising mechanistic potential. It quickly attracted the attention of Novo Nordisk and was officially incorporated into its R&D pipeline in March 2025.
ActRII
ActRII is an activin receptor expressed in both adipose and muscle cells. Activation of this signaling pathway leads to fat accumulation and muscle atrophy. Therefore, inhibitors targeting this pathway hold potential to reduce fat mass while increasing muscle composition. Mechanistically, ActRII-based therapies are being explored as promising candidates for next-generation metabolic interventions.
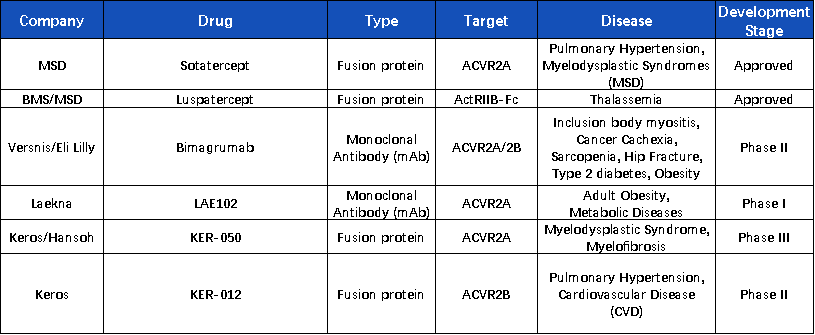
Notably, the druggability of the ActRII target has already been validated in indications such as Luspatercept and Sotatercept. Given the pathway’s complex biological functions, efforts are ongoing to expand its therapeutic applications. One of the most promising directions is its potential to simultaneously reduce fat and increase muscle mass, which has already influenced the development strategies of several investigational drugs.
Eli Lilly’s ActRII antibody, Bimagrumab, is the first to enter clinical trials with obesity as the primary indication. In a Phase II study, Bimagrumab demonstrated preliminary efficacy in increasing muscle mass and reducing fat. At week 48, total body fat mass was reduced by 20.5% in the treatment group versus 0.5% in the control group; lean body mass increased by 3.6% vs. a decrease of 0.8%; HbA1c levels decreased by 0.76% vs. an increase of 0.04%; and body weight decreased by 6.5% vs. 0.8%.
Moreover, no weight regain was observed within 12 weeks after treatment discontinuation. Reported side effects of Bimagrumab to date include muscle cramps and diarrhea, which mostly occurred early in treatment and were generally mild. Data from the Phase II trial comparing Bimagrumab in combination with semaglutide versus semaglutide monotherapy is expected to be presented at the upcoming ADA conference.
In China, Laekna Therapeutics' LAE102, an ActRIIA-targeting antibody, has also gained backing from Eli Lilly for its potential in body composition modulation. Eli Lilly is supporting and accelerating the clinical development of LAE102 for obesity treatment in the U.S., while Laekna retains the global rights to LAE102 and is open to future partnership opportunities.
In a completed Phase I single ascending dose (SAD) study in China, LAE102 demonstrated strong target engagement, with a single dose leading to a significant and sustained increase in activin A levels. On May 28, 2025, Laekna Therapeutics announced that the first participant has been dosed in the U.S. Phase I clinical trial of LAE102, a selective anti-ActRIIA monoclonal antibody developed independently by the company.
Conclusion
Detailed data from this study will be presented at the upcoming ADA meeting. Laekna is advancing a robust, independently developed pipeline targeting the ActRII pathway. LAE103, a selective antibody targeting ActRIIB, and LAE123, a dual inhibitor of ActRIIA and ActRIIB, have both entered IND-enabling studies aimed at exploring innovative therapies for muscle-related and critical illnesses.
From the rise of GLP-1 to the advancement of amylin, and now the exploration of emerging targets such as ACSL5 and ActRII, the development of anti-obesity drugs is rapidly shifting from simple weight management to a new paradigm focused on metabolic optimization, muscle preservation, and long-term health.
The next generation of standout therapies will not only promote weight loss — they will aim for healthier, more sustainable outcomes. This multidimensional race spanning science, capital, and clinical application is only just beginning.
Genomeditech is dedicated to supporting drug research and development by offering a wide range of specialized products and services designed to meet diverse discovery needs. By providing relevant stable cell lines and reporter cell lines for GCGR, GLP1R, GIPR, ACTRII, and AMY/CALCR, Genomeditech helps accelerate drug screening and optimization processes.
Reference
Abbvie. (2025). ABBVie and Gubra announce license agreement to develop an Amylin analog for the treatment of obesity. AbbVie News Center. https://news.abbvie.com/2025-03-03-AbbVie-and-Gubra-Announce-License-Agreement-to-Develop-an-Amylin-Analog-for-the-Treatment-of-Obesity
ADA. (2024). 85th Scientific Sessions | ADA. https://professional.diabetes.org/scientific-sessions
AstraZeneca. (n.d.). Our pipeline. https://www.astrazeneca.com/our-therapy-areas/pipeline.html
Heymsfield, S. B., Coleman, L. A., Miller, R., Rooks, D. S., Laurent, D., Petricoul, O., Praestgaard, J., Swan, T., Wade, T., Perry, R. G., Goodpaster, B. H., & Roubenoff, R. (2021). Effect of Bimagrumab vs Placebo on Body Fat Mass Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity. JAMA Network Open, 4(1), e2033457. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33457
Ji, L., Jiang, H., Bi, Y., Li, H., Tian, J., Liu, D., Zhao, Y., Qiu, W., Huang, C., Chen, L., Zhong, S., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Lian, Q., Yang, P., Lv, L., Gu, J., Liu, Z., Deng, H., ... Qian, L. (2025). Once-Weekly Mazdutide in Chinese Adults with Obesity or Overweight. New England Journal of Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa2411528
Laekna. (2025). Laekna announced first subject dosed in Phase I clinical trial of LAE102 in U.S. for the treatment of obesity. https://en.laekna.com/new/469.html
Laekna. (2025). Laekna will showcase multiple internal discovery achievements on targeting ACTRII receptors at ADA 2025. https://en.laekna.com/new/468.html
Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. (2024). Lexicon to present preclinical IN VIVO efficacy data demonstrating ability of new investigational compound to enhance and maintain Semaglutide-Promoted weight loss. https://investors.lexpharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lexicon-present-preclinical-vivo-efficacy-data-demonstrating
Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. (2025). Lexicon Pharmaceuticals announces exclusive license agreement with Novo Nordisk for LX9851. https://investors.lexpharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lexicon-pharmaceuticals-announces-exclusive-license-agreement
Manalac, T. (2024). Lilly partners with Chinese biotech to advance Muscle-Sparing Obesity treatment. BioSpace. https://www.biospace.com/business/lilly-partners-with-chinese-biotech-to-advance-muscle-sparing-obesity-treatment
Novo Nordisk. (2024, December 20). Novo Nordisk A/S: CagriSeMa demonstrates superior weight loss in adults with obesity or overweight in the REDEFINE 1 trial. https://www.novonordisk.com/news-and-media/news-and-ir-materials/news-details.html?id=915082
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. (2025). Regeneron Expands Clinical-Stage Obesity Portfolio with Strategic In-Licensing of Novel Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist https://investor.regeneron.com/news-releases/news-release-details/regeneron-expands-clinical-stage-obesity-portfolio-strategic/
Roche. (2025). Roche enters into an exclusive collaboration & licensing agreement with Zealand Pharma to co-develop and co-commercialise Petrelintide as a potential foundational therapy for people with overweight and obesity. https://www.roche.com/media/releases/med-cor-2025-03-12
Taylor, N. (2025). Eli Lilly’s phase 1 amylin data impress analysts, pairing 11% weight loss with tolerable profile. Fierce Biotech. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/eli-lillys-phase-1-amylin-data-impress-analysts-pairing-11-weight-loss-tolerable-profile