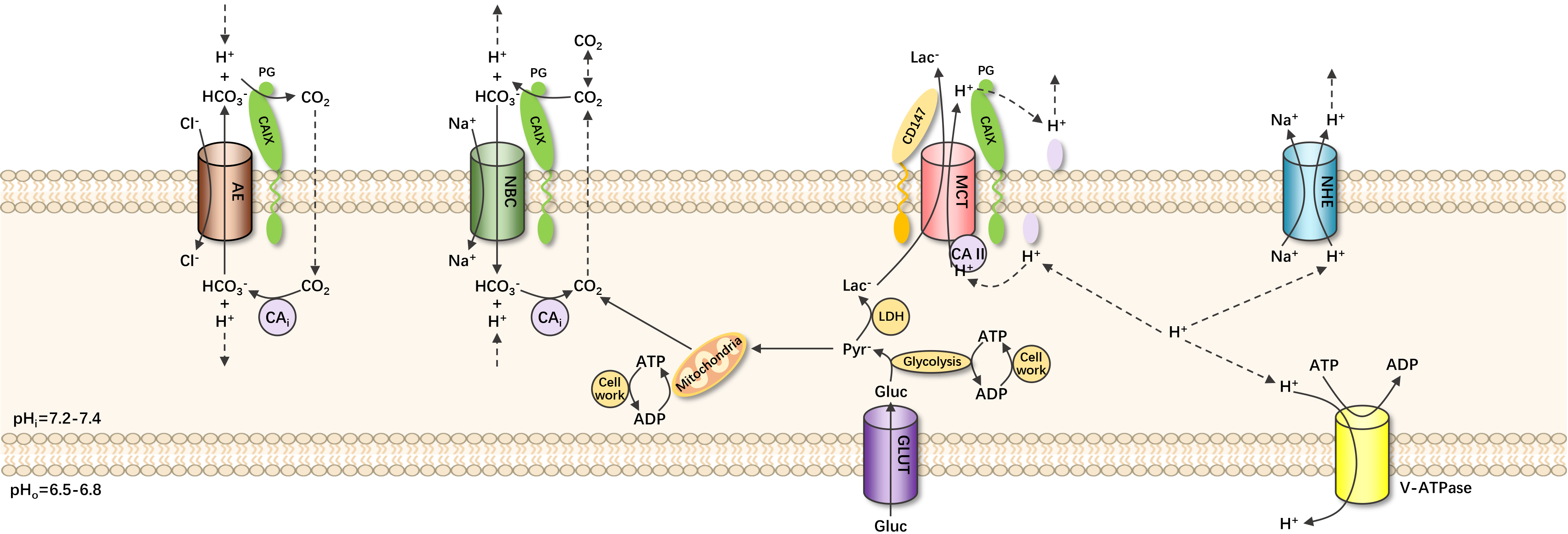
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is a member of the carbonic anhydrase family, enzymes that rapidly convert carbon dioxide and water to produce carbonate, protons, and bicarbonate ions as end products. These enzymes play a vital role in regulating pH in normal tissues within cells and are expressed abundantly in all mammalian tissues. Due to its stability and membrane localization, CAIX is one of the most hypoxia-inducible genes and has become a reliable hypoxia tissue marker. CAIX also serves as an important diagnostic marker for various cancers, especially renal cell carcinoma (RCC).