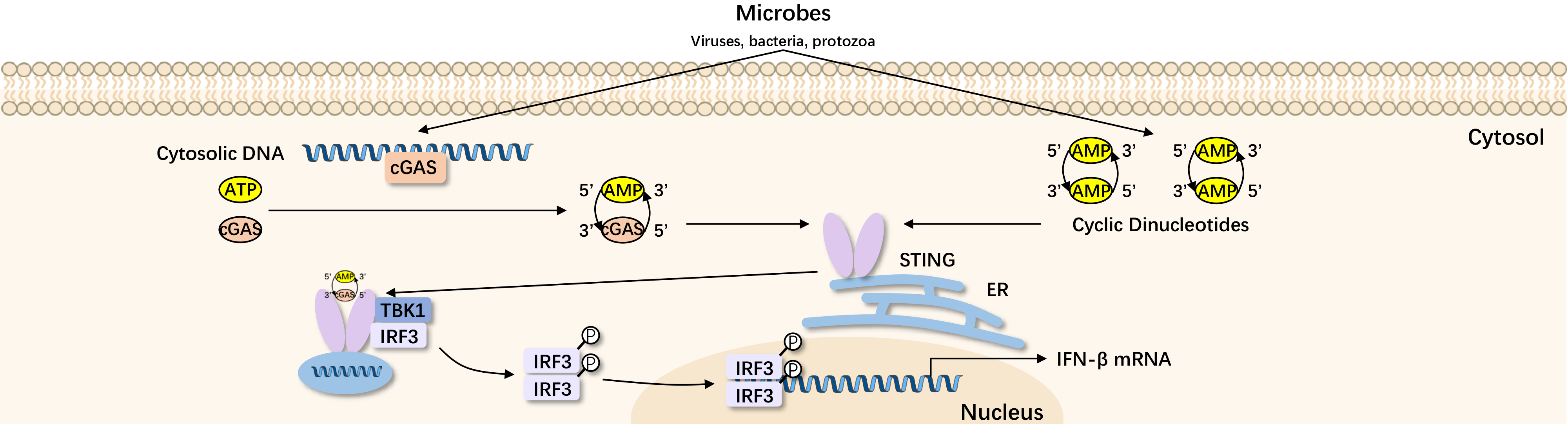
Interferon gene stimulator (STING) is a key regulatory molecule in the innate immune signaling pathway, acting as a crucial connecting protein for cytoplasmic DNA virus and bacterial-derived nucleic acid-triggered signal transduction. STING, as a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor (PRR), plays an important role in regulating the body's response to pathogens, tumors, or self-DNA in the central pathway of the innate immune signaling.
In mammals, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) in the cytoplasm can recognize DNA and catalyze the synthesis of non-classical cyclic dinucleotide - cyclic AMP-GMP (cGAMP) to activate the transmembrane protein STING on the endoplasmic reticulum. Activated STING is transported to the Golgi apparatus for palmitoylation, recruiting and activating TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), further activating interferon regulatory factor IRF3, which forms homodimers, translocates into the nucleus, binds to interferon stimulation response elements (ISRE), produces IFN-α/β, and triggers a signal cascade. The activation of STING can also induce the production of NF-kB-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines, but the specific regulatory mechanisms are still not fully understood. In addition to 2'3'-cGAMP, invading bacteria typically secrete a type of cyclic dinucleotide (CDNs), which have been shown to directly bind to STING.