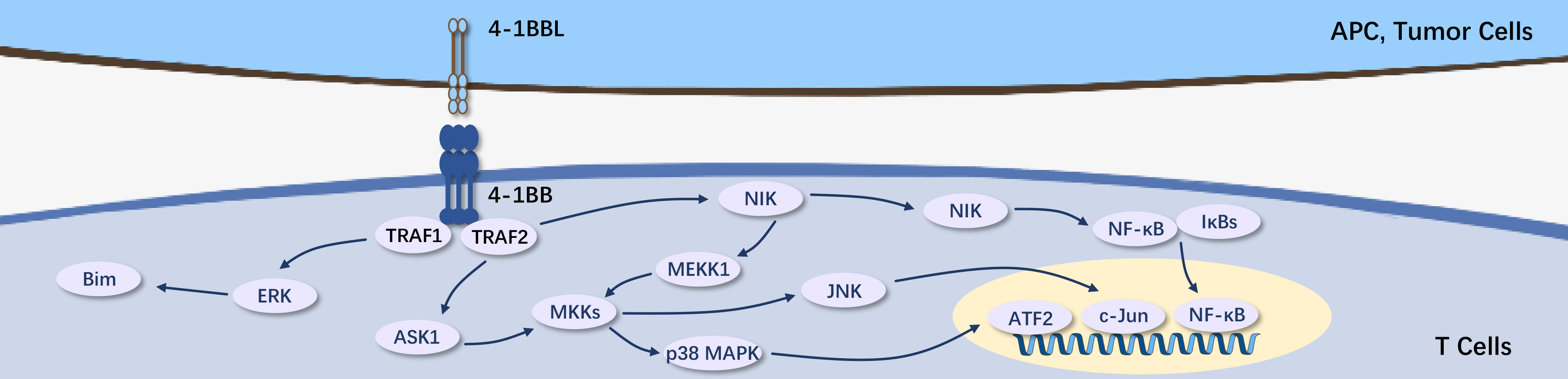
4-1BB, also known as CD137 or TNFRSF9, is an inducible co-stimulatory receptor belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It is expressed in T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and cells of the innate immune system. The interaction between 4-1BB and its ligand (4-1BBL) promotes cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production. Current drug development targeting 4-1BB is mainly for treating inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Agonistic antibodies targeting 4-1BB have shown promising progress in treating inflammation and autoimmune diseases, while combination therapy targeting 4-1BB along with immune checkpoints or co-stimulatory targets holds potential for enhanced anti-tumor effects.
Drug development targeting 4-1BB can be broadly categorized into two groups: those for treating inflammation or autoimmune diseases, and those for cancer treatment. Unlike traditional targeted therapies for inflammation or autoimmune diseases, most drugs developed for treating these conditions involving 4-1BB are agonistic antibodies rather than inhibitory ones. This difference could be attributed to their potential to induce excessive activation of natural or induced Treg cells, or IFNγ-induced regulatory capabilities in CD8+ T cells. Progress in developing agonistic targeted drugs based on this principle is promising but requires caution.
However, the progress of 4-1BB mAbs in cancer treatment has been less satisfactory. The initial agonistic therapeutic antibodies targeting 4-1BB, such as Pfizer's Utomilumab and BMS's Urelumab, have shown either low efficacy or significant hepatotoxicity. Currently, both are being developed in combination therapy with other drugs.