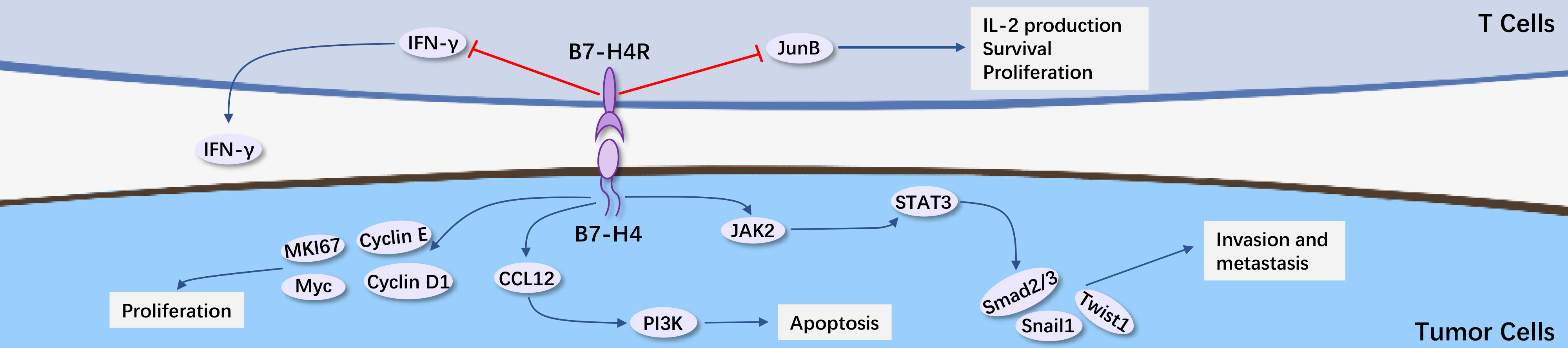
B7H4, also known as B7-S1 or VTCN1, is a type I transmembrane protein. In normal healthy tissues, B7H4 is expressed at relatively low levels. However, in many solid tumors such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and endometrial cancer, it is highly expressed, and its expression level is inversely correlated with prognosis.
Belonging to the B7 family, experimental evidence has shown that it can bind to T cells and inhibit their activity. As it is overexpressed on the surface of tumor cells and correlates negatively with patient treatment benefits, while also serving as a T cell coinhibitory checkpoint, B7H4 appears to be an ideal target for treating solid tumors.