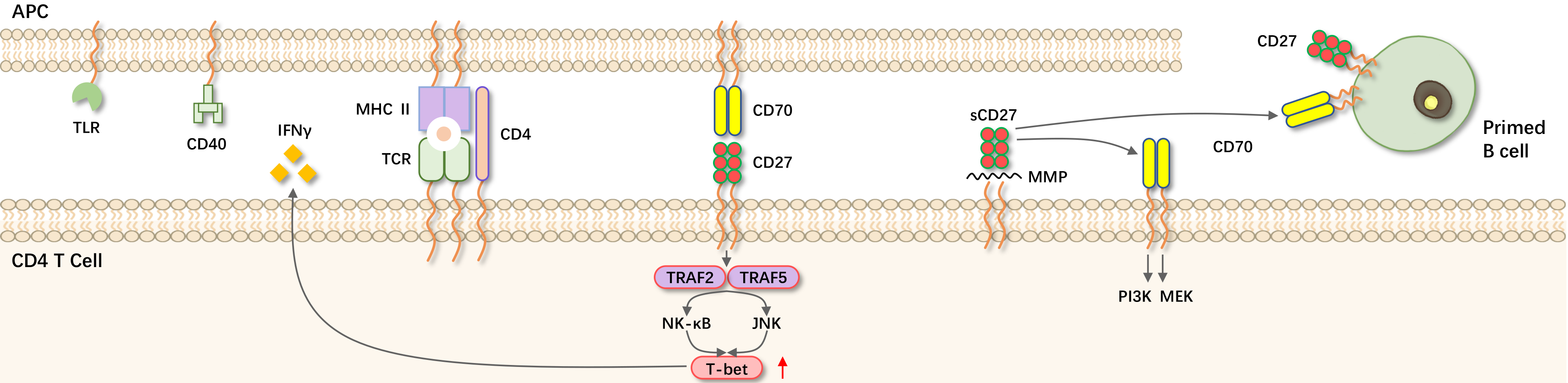
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 7 (TNFRSF7, CD27, expressed directly by T, B, and NK cells and their precursors) and its unique known ligand CD27L (TNFSF7, CD70, constitutively expressed only after activation of immune cells) provide co-stimulatory signals that promote T cell activation, differentiation, and survival, leading to functional immune responses. When the T cell receptor (TCR) recognizes peptide/MHC complexes presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), CD80/CD86 is upregulated and CD70 is newly induced. These ligands respectively trigger CD28 and CD27 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, leading to cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses that eliminate all tumor cells.
Current clinical trials using CD27-targeting agents consist of agonistic antibodies and are mainly focused on Celldex Therapeutics and Aduro. From the development experience of Varlilumab and MK-5890, it is evident that while using CD27 agonistic antibodies alone yields good efficacy, it can lead to depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and may not maximize therapeutic effects. The combined use of various alternative anti-tumor activity synergistic mechanisms can enhance efficacy to a greater extent, suggesting that the development of CD27-related multispecific antibodies may be a better option.