B7-H3 (CD276) is the most recently identified ligand molecule of the B7 family, a type I transmembrane glycoprotein consisting of an extracellular domain, transmembrane domain, and short intracellular domain. B7-H3 possesses classic extracellular IgV and IgC domains.
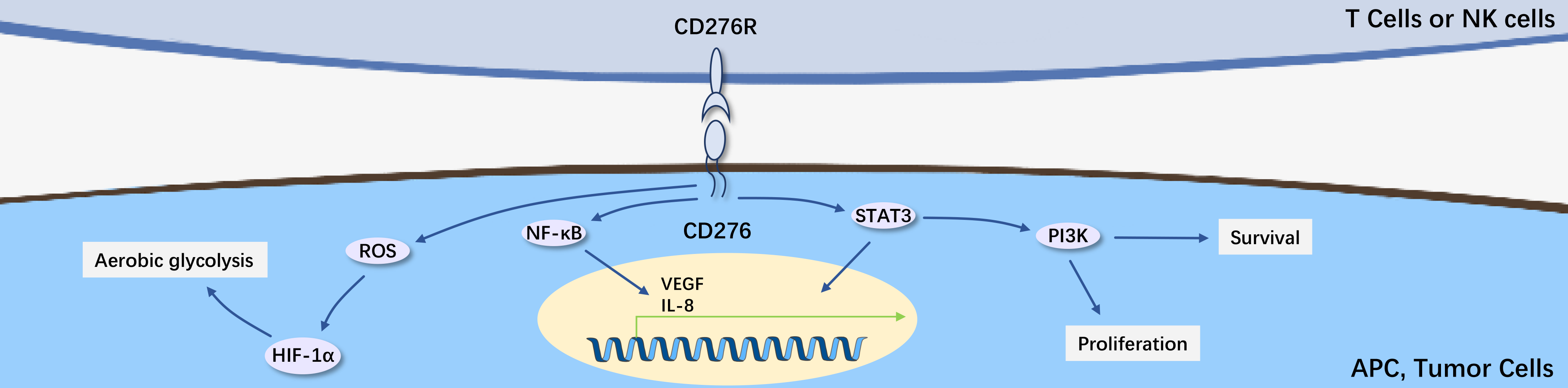
B7-H3 is constitutively expressed on non-immune cells. Additionally, it can be induced on the surface of immune cells (such as DCs, monocytes, and B cells). B7-H3 plays a critical role in regulating T cell immune responses. B7-H3 negatively regulates the activity of key transcription factors (including NFAT, AP-1, and NFκB), reducing IL-2 production, inhibiting proliferation and activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and suppressing Th1 cells and the Th1 cytokine IFN-γ. However, B7-H3 has a positive effect on Th2 cells and Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10) as well as Th17 cells and the Th17 cytokine IL-17. Despite the controversial immune functions of B7-H3, it may play an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by modulating different T cell subsets.
Currently, various anti-B7-H3 therapies are in preclinical or clinical trials, including monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), CAR-T cells, etc., but none have been approved for cancer treatment. DS-7300 is an ADC drug targeting B7-H3 developed by the Japanese pharmaceutical company Daiichi Sankyo using DXd technology, which has progressed to Phase II clinical trials. SCRI-CARB7H3 is a CAR-T cell therapy drug developed by Seattle Children's Hospital, currently in Phase I clinical trials.