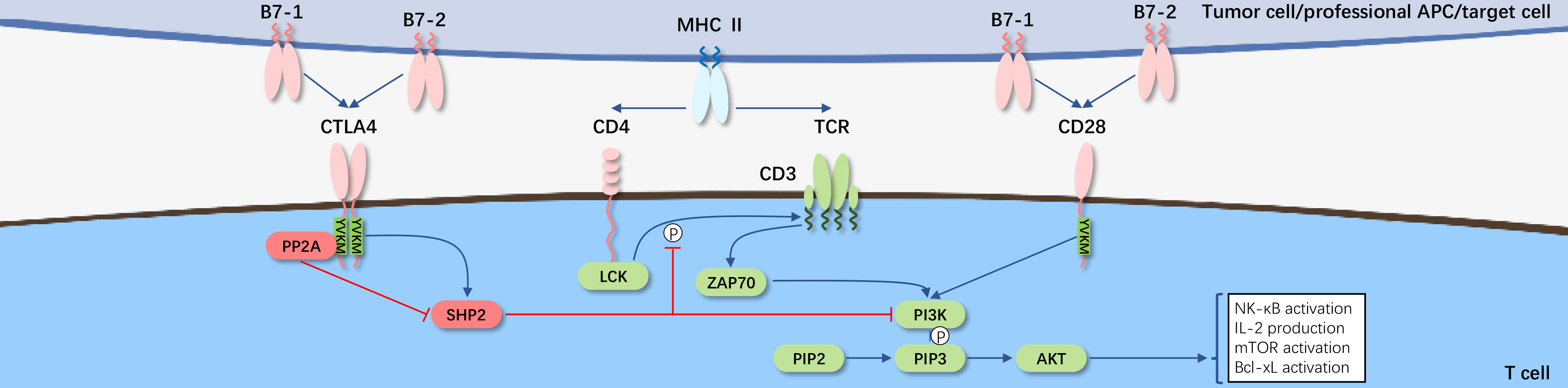
CD28, as the first discovered co-stimulatory receptor, is the founding member of the co-stimulatory molecule subfamily characterized by an extracellular variable immunoglobulin-like domain. CD28 primarily functions as the "second signal" (binding to B7-1/B7-2 on the surface of target cells) to lower the threshold required for effective activation of T cells, strengthening the "first signal" (TCR-CD3 complex recognition and binding to MHC-peptide on target cells), thus further developing T cells to proliferate into immunologically functional cells. Concurrently, CD28 and the co-inhibitory receptor CTLA-4, along with their shared ligands B7-1 and B7-2, constitute the most distinctive regulatory pathway for T cells, serving as paradigms for other co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory pathways.
Given the importance of CD28 co-stimulation in T cell activation, modulating the immune response through activation or blockade of the CD28/B7-1 (CD80)/B7-2 (CD86) pathway holds promise: it can prevent inappropriate T cell activation rejection reactions during transplantation or treat T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Currently, clinical drug development mainly focuses on 3 aspects: CD28-related target fusion protein drugs, monoclonal antibody drugs, and multi-specific antibody drugs, with the primary goal of modulating T cell activation by stimulating/inhibiting the CD28 axis, improving the prognosis of patients with autoimmune/inflammatory diseases.