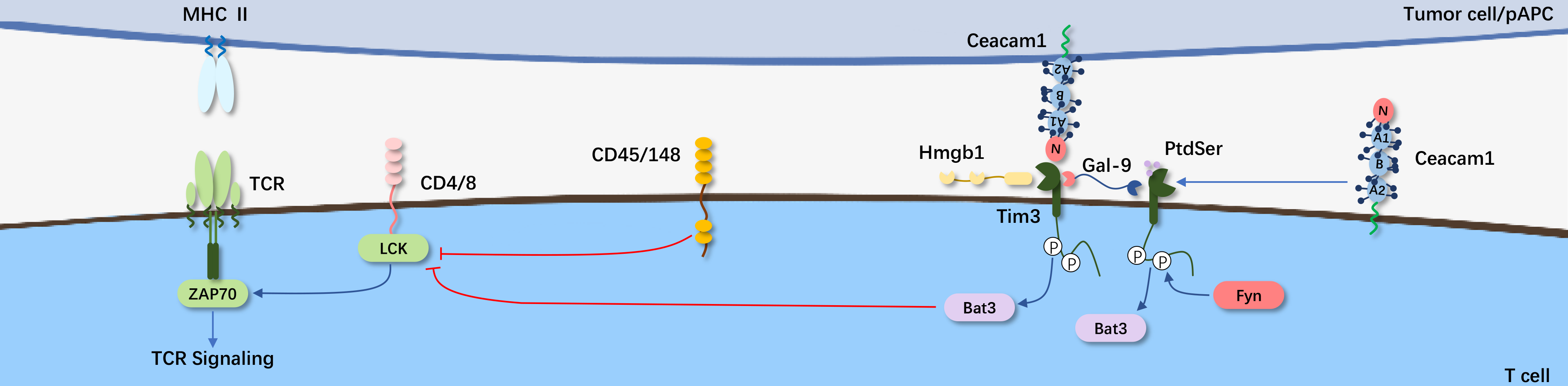
The immune checkpoint protein TIM3 is a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity and a member of the TIM family. TIM3 is a type I membrane glycoprotein expressed in terminally differentiated CD4+ T cell subsets such as Th1 cells, Th17 cells, Tregs, and CD8+ T cell subsets like type 1 CD8+ T cells (Tc1), but not in Th2 cells.
TIM3 consists of three parts: an extracellular region containing an IgV domain with FG-CC' loops and N-linked glycosylation, a mucin domain with O-linked glycosylation sites, and a stalk domain with N-linked glycosylation; a transmembrane region; and an intracellular region with a cytoplasmic tail containing five tyrosine residues.
TIM3 has been shown to regulate innate and adaptive immune responses, potentially playing a positive or negative role as an immune modulator. The different effects of TIM3 may depend on the various immune antigens in different cells expressing this receptor and in the tumor microenvironment. Studies have found that blocking TIM-3 alone can inhibit tumor growth in various mouse tumor models (CT-26, MC38, etc.). However, combined blockade of TIM-3 with CTLA-4/PD-1 has a more significant anti-cancer effect.