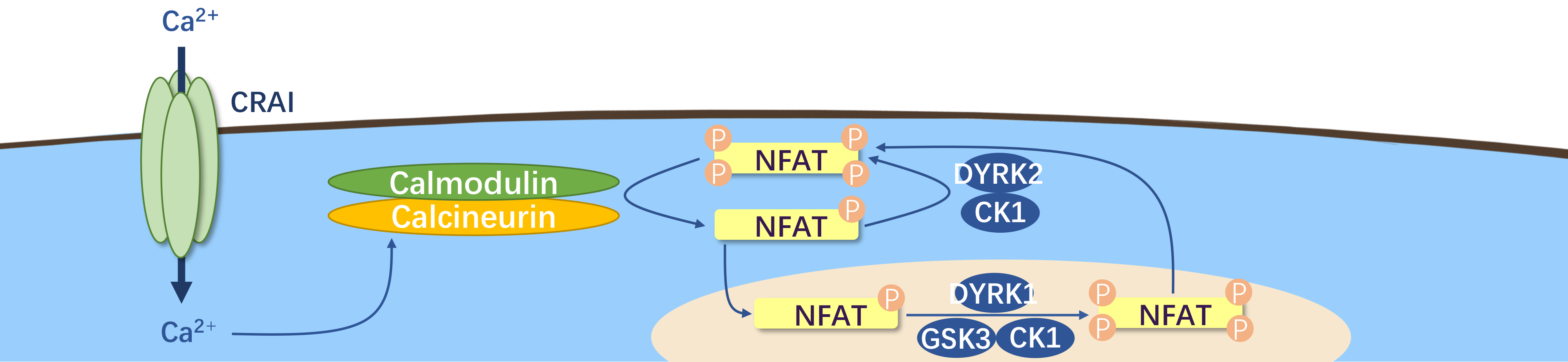
Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells (NFAT) is a transcription factor family that plays a crucial role in inducing gene transcription during immune responses. Apart from T cells, these proteins are also expressed in various immune cells such as B lymphocytes, mast cells, and eosinophils. Their activity is regulated by the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin.
NFAT is a multifunctional transcription factor involved in regulating T cell activation, differentiation, and self-tolerance. It is expressed in various immune cells and induces the transcription of cytokines and other genes in the body's immune response. Numerous studies have linked NFAT activation to the development of various acute and chronic diseases like asthma, Alzheimer's disease, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, myocarditis, highlighting its increasing importance.