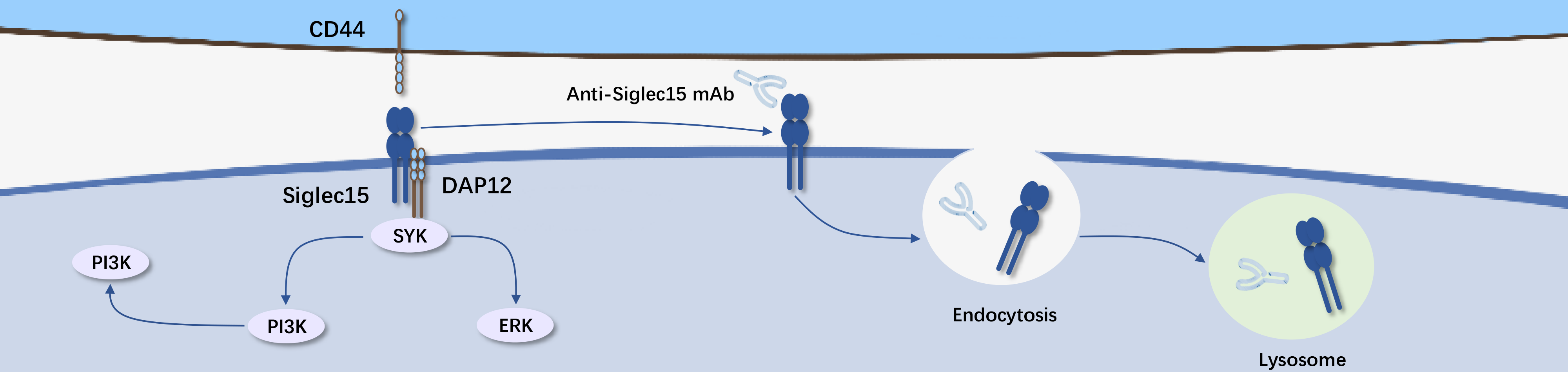
Siglec-15 is a member of the Siglec family and possesses unique molecular characteristics compared to many known checkpoint inhibitors. Siglec-15 mRNA is expressed at low levels in most normal tissues and immune cells, but is expressed in various tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs).
Studies have shown that Siglec-15 can act as a macrophage receptor, recognizing the commonly expressed sialyl-Tn antigen in tumors, and may promote tumor cell development by inducing the cancer-promoting cytokine TGF-β-mediated tumor microenvironment through the DAP12-Syk pathway. Siglec-15 directly inhibits NF-κB/NFAT signaling by binding to CD44, mediates and suppresses T cell proliferation and cytokine production through IL-10, thereby inhibiting anti-tumor immunity and promoting tumor growth. In vitro, Siglec-15 can independently inhibit the proliferation and activation of antigen-specific T cells, regardless of macrophages or IL-10.
Research suggests that Siglec-15 has immune regulatory functions similar to PD-L1, but the expression of Siglec-15 and PD-L1 is mutually exclusive. With the current efficacy of tumor immunotherapy hovering around 20%, Siglec-15 is likely to be a complementary therapeutic target, providing new treatment options for patients resistant to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy.