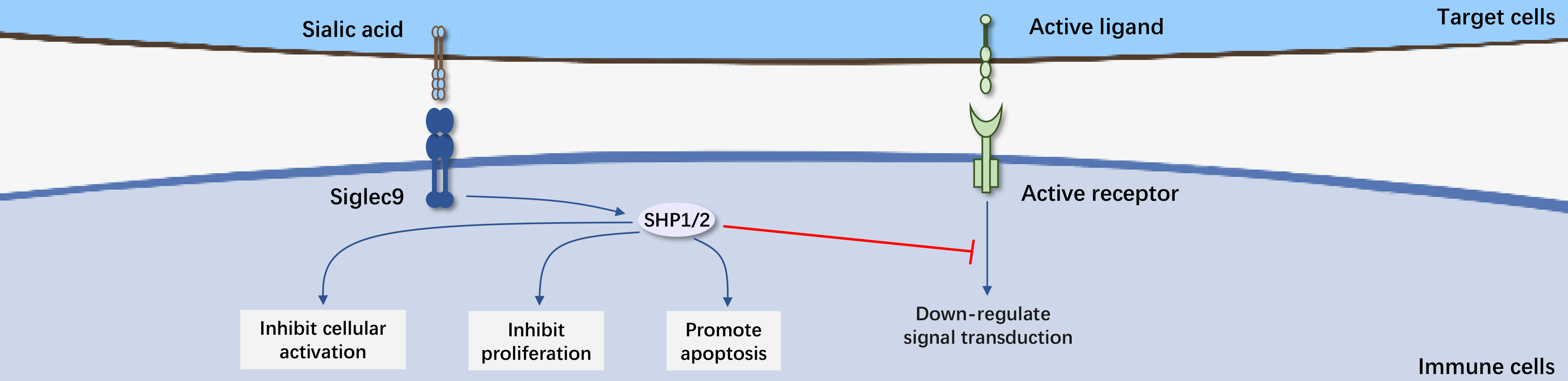
Siglec-9 is a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) family, belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF). Siglec-9 shares high homology with many members of the Siglec family, including Siglec-7 (80%), Siglec-8 (72%), Siglec-5 (65%), and CD33 (64%). This high homology is also conserved in the extracellular Ig-like domains. Siglec-9 consists of a hydrophobic signal peptide, an N-terminal Ig-like V-type domain, two Ig-like C2-type domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. Siglec-9 contains an ITIM motif in the cytoplasm, which mediates inhibitory signaling. Siglec-9 is mainly expressed in tumor-infiltrating T cells, NK cells, macrophages, etc. By binding to sialic acid on the surface of tumor cells, it directly inhibits T cell activation.
Recent studies have shown that the peripheral blood of various cancer patients has a significantly reduced proportion of Siglec-9+ NK cell subsets, accompanied by high expression of Siglec-9 ligands in tumor tissues. When the ligand binds to its receptor, it suppresses the cytotoxicity of NK cells, allowing tumor cells to evade innate immune surveillance. Additionally, high expression of Siglec-9 ligands has been found in chronic sinusitis tissues, which may be closely related to the activation of the nuclear transcription factor NK-κB signaling pathway. The binding of overexpressed Siglec-9 ligands to receptors inhibits the activity of neutrophils and helps the body control pathological airway inflammation.