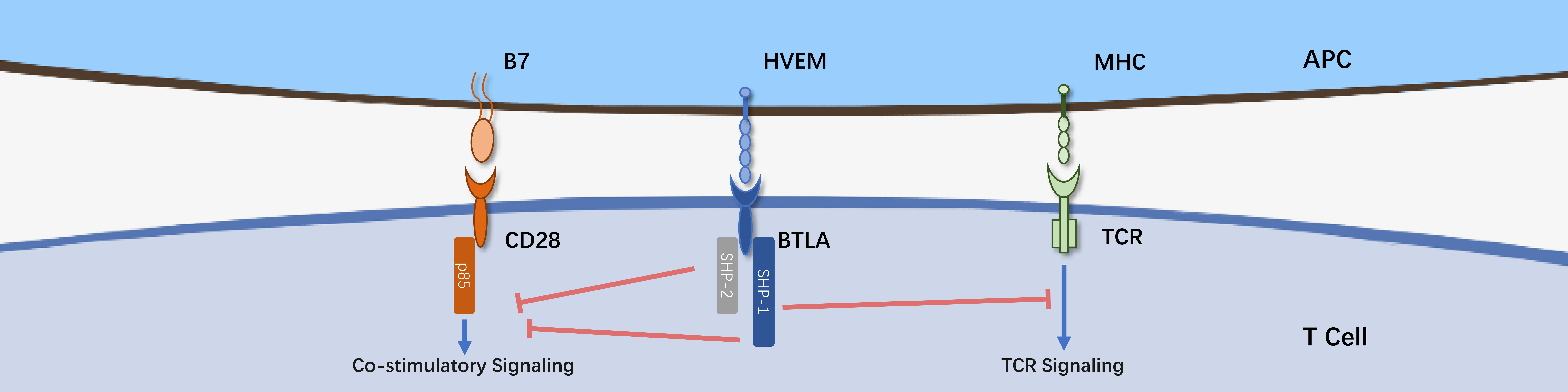
BTLA is a glycoprotein containing an immunoglobulin domain, expressed on T cells, resting B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and a small subset of NK cells. As an inhibitory receptor on T cells, anti-BTLA therapy can lead to T cell proliferation, and BTLA gene knockout mice show heightened immune activation. HVEM is a tumor necrosis factor receptor identified as the natural ligand of BTLA in mice and humans. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) expressing HVEM can induce BTLA-dependent T cell suppression.
The interaction between BTLA/HVEM plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation, autoimmunity, and anti-tumor responses. In melanoma patients, BTLA is expressed on tumor-specific T cells in circulation and metastatic lymph nodes. HVEM is highly expressed in most melanoma cell lines and metastatic melanoma samples. The interaction between tumor-specific T cells expressing BTLA and melanoma cells expressing HVEM leads to T cell suppression, which can be reversed by blocking BTLA antibodies. In cell-based assays from melanoma patients, concurrent blockade of BTLA and the PD-1 pathway significantly increases the number and function of tumor-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes, surpassing the effect of PD-1 blockade alone, suggesting BTLA as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy development.
Currently, this target has garnered attention and development from some new drug development companies. In March 2019, Junshi Biosciences announced the development of the world's first specific recombinant humanized IgG4κ monoclonal antibody JS004 targeting BTLA, gaining FDA acceptance for clinical trials in the treatment of advanced unresectable or metastatic solid tumors (including lymphoma). In 2020, this antibody also received approval for clinical trials domestically, and it is currently undergoing clinical trials both domestically and internationally.