Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2), is a monomeric glycoprotein that acts as a cytokine by secreting macrophages, T cells, mast cells, natural killer cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. Unlike granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, GM-CSF specifically promotes the proliferation and maturation of neutrophils, affecting a wider range of cell types, particularly macrophages and eosinophils.
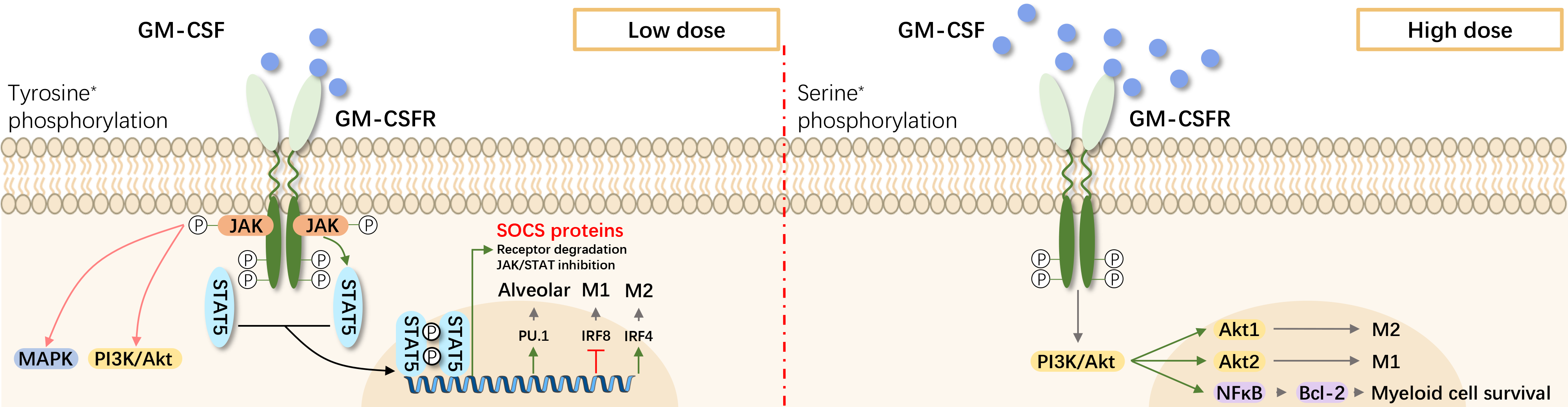
The GM-CSF receptor consists of α (CDw116; GM-CSFRα) and β (GM-CSFRβc) chains, with βc chain shared among GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5. Binding of GM-CSF initiates JAK2 autophosphorylation and receptor downstream signaling. JAK2 subsequently activates STAT5 and MAPK. Non-JAK2 pathways are also involved in GM-CSF receptor signaling. The hematopoietic-specific transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) is a key signaling molecule adopting dendritic cell (DC)-like characteristics in precursors cells (e.g., monocytes) upon GM-CSF treatment.
As a significant component of the cytokine storm in COVID-19, targeting GM-CSF with antibodies has shown promising clinical results. Meanwhile, several antibody drugs have entered clinical stages for autoimmune diseases.