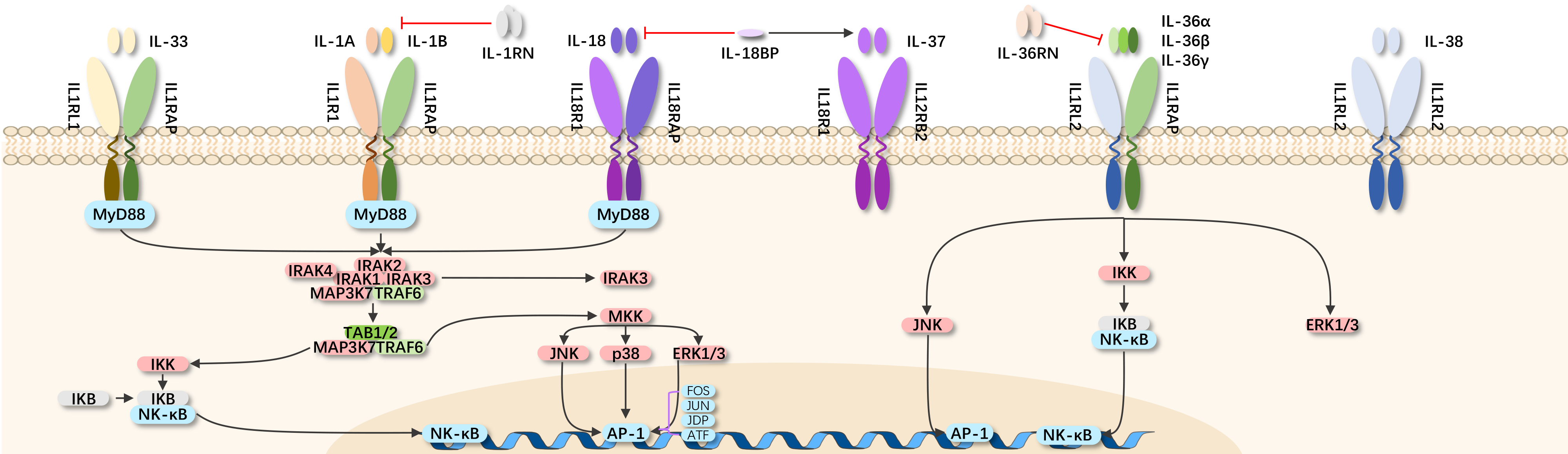
The IL-1 family mainly consists of two agonists: IL-1α and IL-1β; one endogenous antagonist: IL-1RA; two receptors: IL-1RI and IL-1RII. The IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) forms a complex with IL-1R1 after binding with IL-1, serving as an essential receptor partner in signal transduction.
IL-1 is a cytokine released by various cell types, acting in an autocrine and/or paracrine manner to stimulate multiple signaling pathways. IL-1α and IL-1β signal through IL-1RI. Binding with IL-1RII does not lead to cell signaling, making it a decoy receptor. When IL-1 binds with IL-1RI, IL-1RAcP is recruited to the cell membrane to form a high-affinity receptor complex, initiating intracellular signal transduction. IL-1RA binds with IL-1 receptors, preventing the interaction between IL-1 and its receptor, acting as a natural IL-1 inhibitor.
IL-1β, as a key proinflammatory cytokine, is involved in various autoimmune inflammatory responses and cellular activities, including proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Together with IL-1α and IL-18, IL-1β coordinates immune responses through multiple downstream mechanisms. IL-1β regulates IL-6 and TNF-α and activates the vascular adhesion molecule ICAM1.
IL-1β is considered a typical pleiotropic cytokine, affecting almost all cell types, whether acting alone or in combination with other cytokines. It is crucial for cell defense and tissue repair in almost all tissues, associated with pain, inflammation, and autoimmunity. IL-1β also plays a role in neuroprotection, tissue remodeling, and repair.