IL-2 is the first cloned interleukin factor and the first factor approved for tumor therapy, initially named T-cell growth factor (TCGF) and belongs to the type 1 cytokine family.
IL-2 is mainly produced by CD4+ T cells. Regulation of IL-2 gene expression involves various transcription factors including Nuclear Factor of Activated T cells (NFAT), Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB), Octamer-binding protein 1 (POU2F1), High Mobility Group Protein A1 (HMGA1), and FOXP3 protein.
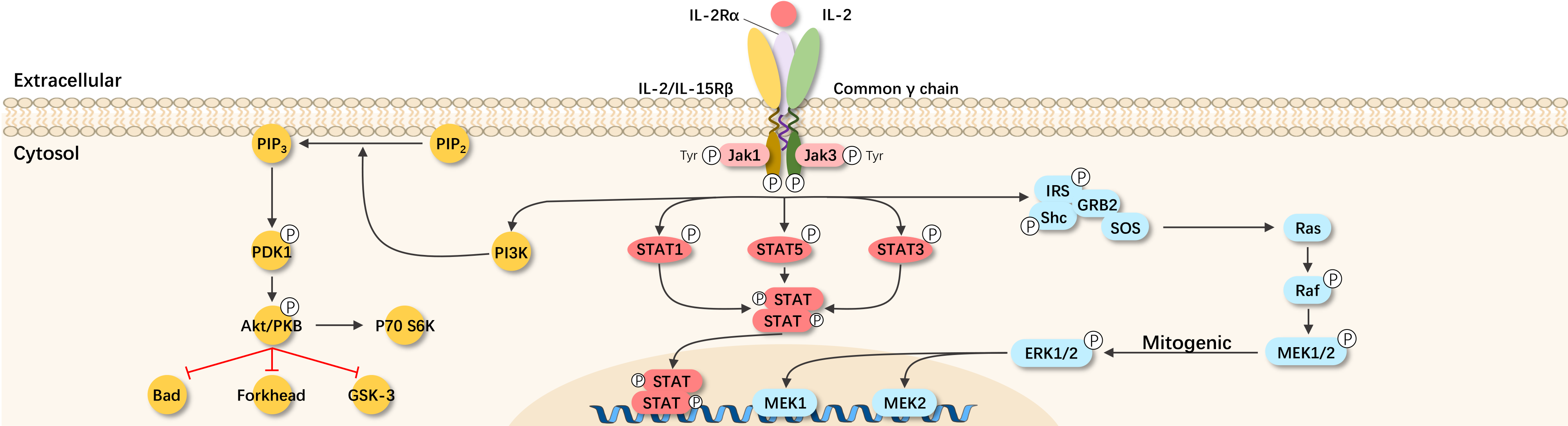
The IL-2 receptor is a heterotrimer composed of α, β, and γ chains, forming the IL-2R consisting of IL-2Rα (CD25), IL-2Rβ (CD122), and IL-2Rγ (CD132). The β/γ chains are essential for downstream signal pathway activation, while α primarily facilitates their binding. When the IL-2 receptor α subunit (IL-2RA) is present alone, its affinity to IL-2 is only one percent of that of the complete IL-2 receptor, resulting in high, intermediate, and low-affinity IL-2Rs.
Initially identified as a T-cell growth factor, IL-2 has been discovered to possess multiple functions including enhancing cell lytic activity, driving Treg cell development, inhibiting immune cell responses, promoting potential cell elimination through activation-induced cell death, and facilitating the differentiation of various effector T cell subsets. Therefore, the biological functions regulated or inhibited by IL-2 are diverse and hold potential therapeutic effects in various diseases.