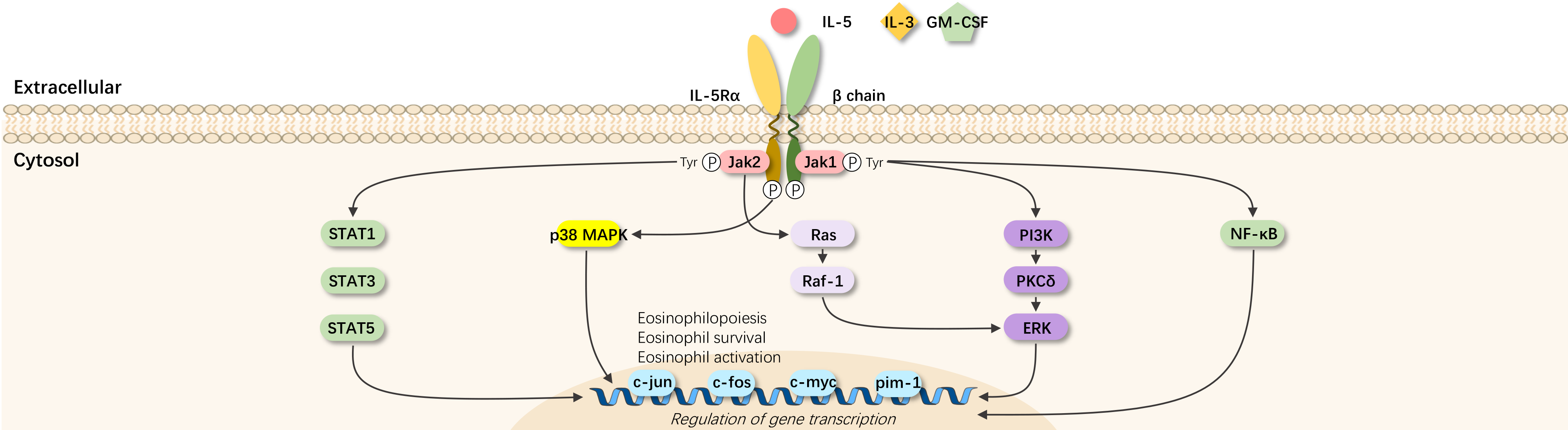
IL-5 is a core cell factor for eosinophilic asthma, involved in the differentiation, activation, proliferation, survival, and recruitment of eosinophils to the airways.
IL-5 selectively binds and activates the receptor IL-5R to transmit signals. The α chain of IL-5R binds with IL-5, while the βc chain is shared with IL-3 and GM-CSF. In the absence of IL-5, the α chain binds with JAK2, and the βc chain binds with JAK1. In the presence of IL-5, the IL-5R α chain and βc chain form a heterodimer with IL-5, activating the intracellular JAK2-STAT1, 3, 5 signaling to initiate a series of gene transcription.
JAK2 activates Lyn and RAF-1 kinases, inhibits eosinophil apoptosis, or induces anti-apoptotic protein BCL-XL through NF-κb dependent signaling. IL-5, via the PI3K, MAPK, NF-κb pathways, participates in the maturation, activation, proliferation of eosinophils, and induction of eosinophil chemotactic factor leukotriene C4. Through the PI3K and MAPK pathways, inflammatory cell factors can be induced, further promoting inflammation.