The interleukin-10 (IL-10) gene is located on chromosome 1q31-32 and is primarily produced by monocytes, T cells (especially Th1 cells), B cells, NK cells, and macrophages. The IL-10 receptor is composed of two IL-10R1 and two IL-10R2 chains. Binding of IL-10 to the receptor complex activates Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2), leading to signal transduction and activation of transcription factors STAT1 and STAT3. Other kinases, such as mitogen-activated protein kinase and heme oxygenase-1, can also be activated.
When IL-10 binds to its cell receptor complex IL-10R1/IL-10R2, it exerts various immunosuppressive functions, initially discovered as an inhibitor of cytokine synthesis in Th1 cells. Further research shows that IL-10 can also inhibit the cytokine production capacity of antigen-presenting cells (macrophages and dendritic cells) and the expression of co-stimulatory molecules (CD80, CD86). IL-10 is considered a key anti-inflammatory cytokine produced by a variety of immune cells and tissue epithelial cells.
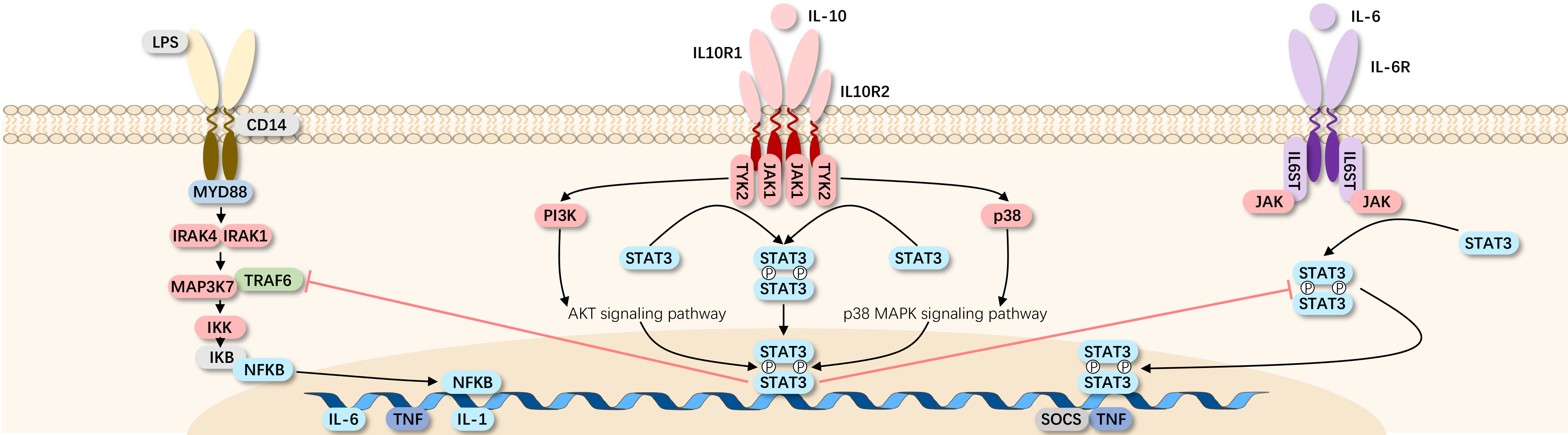
Signaling impairment in the IL-10 pathway is associated with inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with immune pathological changes often accompanying infections. Conversely, overexpression or dysregulation of IL-10 may lead to chronic infections. In certain circumstances, IL-10 can also have immune-stimulating functions, such as in mast cells, B cells, and T cells.














