Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a cytokine naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and human B lymphoblasts (NC-37) in response to antigen stimulation. IL-12 belongs to the interleukin-12 family, which uniquely consists of heterodimeric cytokines including IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, and IL-35. Despite sharing structural features and molecular partners, they mediate various surprising functional effects.
IL-12 is produced by activated antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells, macrophages), promoting the development of Th1 response and serving as a potent inducer for T cells and NK cells to produce IFNγ.
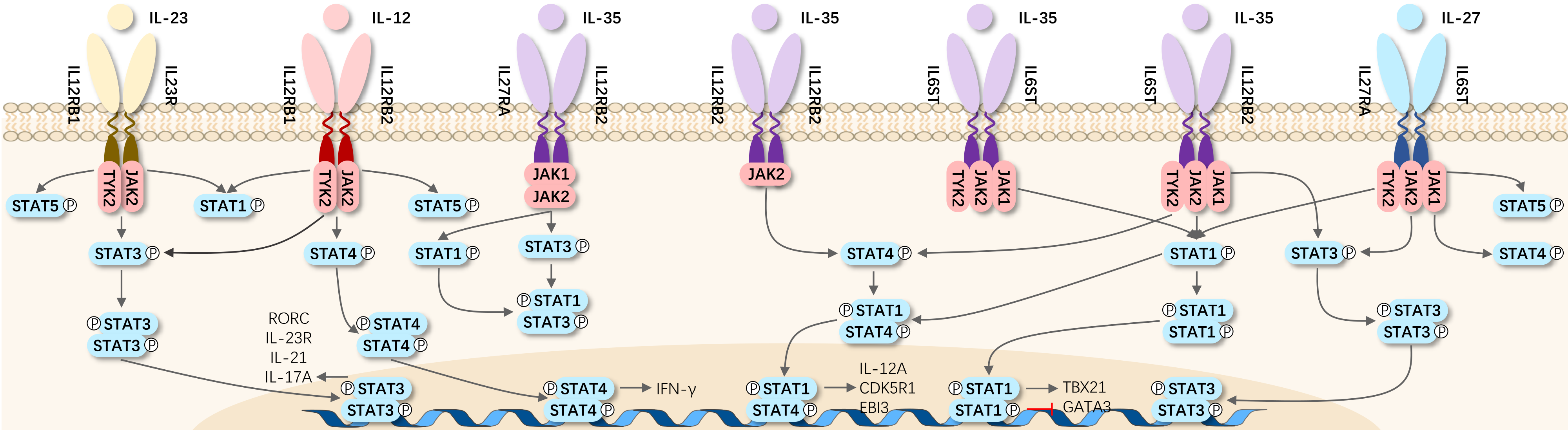
The IL-12 receptor is comprised of two chains, IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2, both of which share significant homology with the common receptor β chain gp130 of IL-6. Co-expression of IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12Rβ2 is essential for generating a high-affinity (50 pM) IL-12 binding site, with IL-12Rβ2 subunit acting as a signaling component of the high-affinity receptor complex. An 85 kDa protein associated with IL-12Rβ1 responds to IL-12 phosphorylation, potentially being another component of IL-12R140. Signaling transduction through IL-12R induces tyrosine phosphorylation, primarily of Janus family kinases JAK2 and TYK2, leading to phosphorylation and activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1), STAT3, STAT4, and STAT5. The specific cellular effects of IL-12 are mainly attributed to its ability to induce STAT4 activation.