IL-17 (IL-17A, CTLA-8) was first cloned in 1993, but its function remained unclear for the following decade. In 2005, the discovery of a new group of CD4+ T helper cells characterized by IL-17 expression brought attention to IL-17. This subset was later named "Th17 cells." Although Th17 cells are generally considered the main source of IL-17, CD8+ cells have also been shown to produce this cytokine, known as "Tc17."
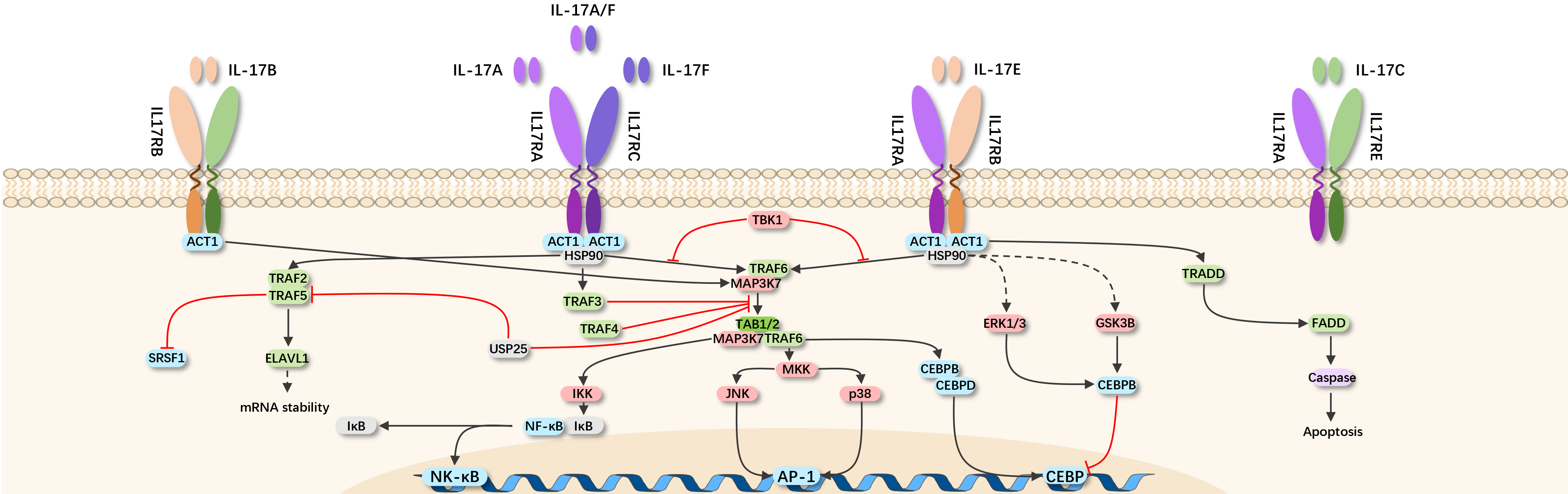
The IL-17 family consists of six structurally related cytokines: IL-17A, IL-17B, IL-17C, IL-17D, IL-17E (IL-25), and IL-17F. IL-17A and IL-17F are closely related, co-expressed in linked genes, and typically produced together by type 17 cells. Similarly, the IL-17R family includes five receptor subunits: IL-17RA, IL-17RB, IL-17RC, IL-17RD, and IL-17RE.
IL-17 signaling begins with the binding of IL-17A/A, IL-17A/F, or IL-17F/F cytokines to their receptors, IL-17RA and IL-17RC. Upon ligand binding, Act1 activates multiple independent signaling pathways mediated by different TRAF proteins. Activation of TRAF6 can trigger NF-κB, C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, and MAPK pathways. The IL-17R-Act1 complex also binds to MEKK3 and MEK5 through TRAF4, inducing ERK5 activation. IL-17 signaling pathways mediated by TRAF6 and TRAF4 lead to the transcription of inflammatory genes, while the ACT1-TRAF2-TRAF5 complex in the IL-17 signaling pathway controls the stability of IL-17 target gene mRNA. Thus, IL-17 upregulates the expression of inflammatory genes by inducing the transcription of new genes or stabilizing the mRNA transcription of target genes.