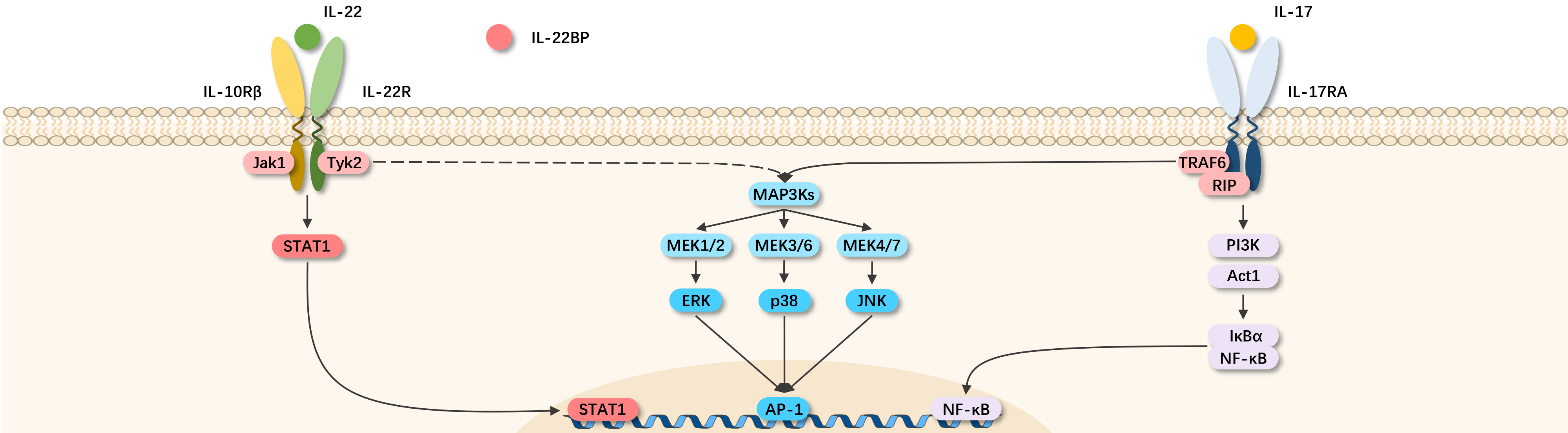
IL-22, discovered in 2000, is a member of the IL-10 family. The IL-22 gene encodes 179 amino acids, and after removing a 33-amino acid signal peptide, the secreted form of IL-22 is 146 amino acids long. The IL-22 receptor is a heterodimer composed of IL-22R1 and IL-10R2. IL-22R1 also acts as a receptor subunit for other IL-10 family cytokines (IL-20 and IL-24). Additionally, a single-chain secreted receptor, IL-22BP, binds to IL-22, thereby blocking its signal. Activation of the JAK1-STAT3 pathway downstream of IL-22R generates corresponding functional effects.
Unlike most interleukins, IL-22 does not directly regulate the function of immune cells. Instead, IL-22 targets cells on external barriers, such as the skin and tissues of the digestive and respiratory systems, as well as organs like the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and joints. IL-22 induces these cells to produce antimicrobial proteins and specific chemokines, with amplification of this effect by IL-17, TNF-α, and IL-1β. IL-22 protects its target cells from damage, inhibits their differentiation, and/or increases proliferation, effects unique to this cytokine. Studies using mouse models suggest that enhancing the IL-22-IL22R system (e.g., through IL-22 application) may have beneficial effects on inflammatory bowel disease, alcoholic liver disease, pancreatic damage, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and organ transplantation.