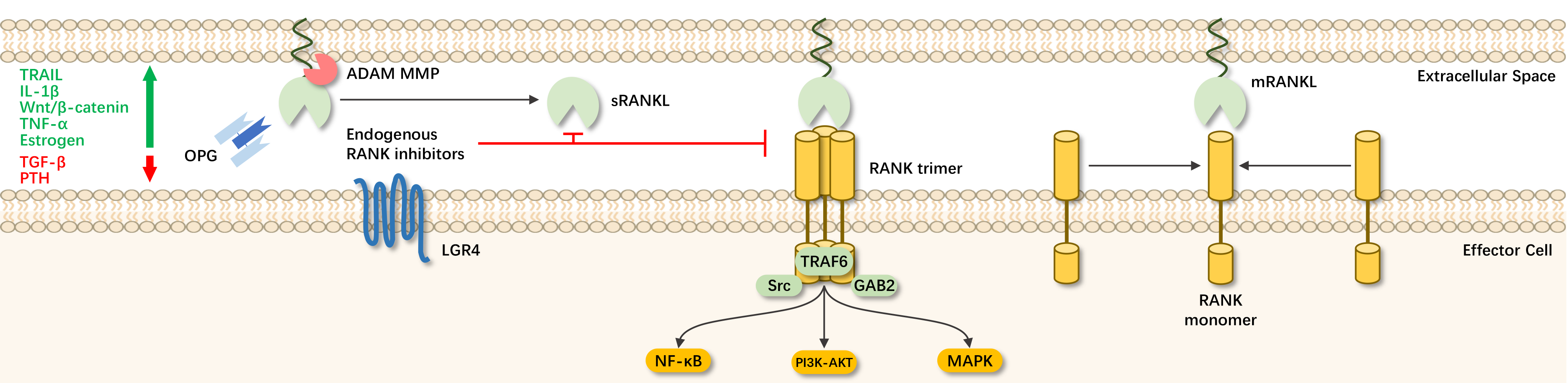
The receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, which is a key factor in the activation of osteoclast differentiation, inducing osteoclast activation, inhibiting osteoclast apoptosis, and can be used for the treatment of osteoporosis.
The RANKL/RANK/OGP system is a typical pathway for RANKL involvement in bone remodeling. RANKL expressed by osteoblasts binds to RANK on osteoclast precursor cells. The binding of RANK to downstream TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) can initiate the transcription of osteoclast production genes, inducing osteoclast precursors to mature into osteoclasts.
Studies have shown that the RANKL/RANK pathway can promote bone metastasis by activating osteoclasts. Inhibiting RANKL can prevent bone resorption and tumor growth caused by metastasis, with RANKL antibodies also holding value in cancer therapy.