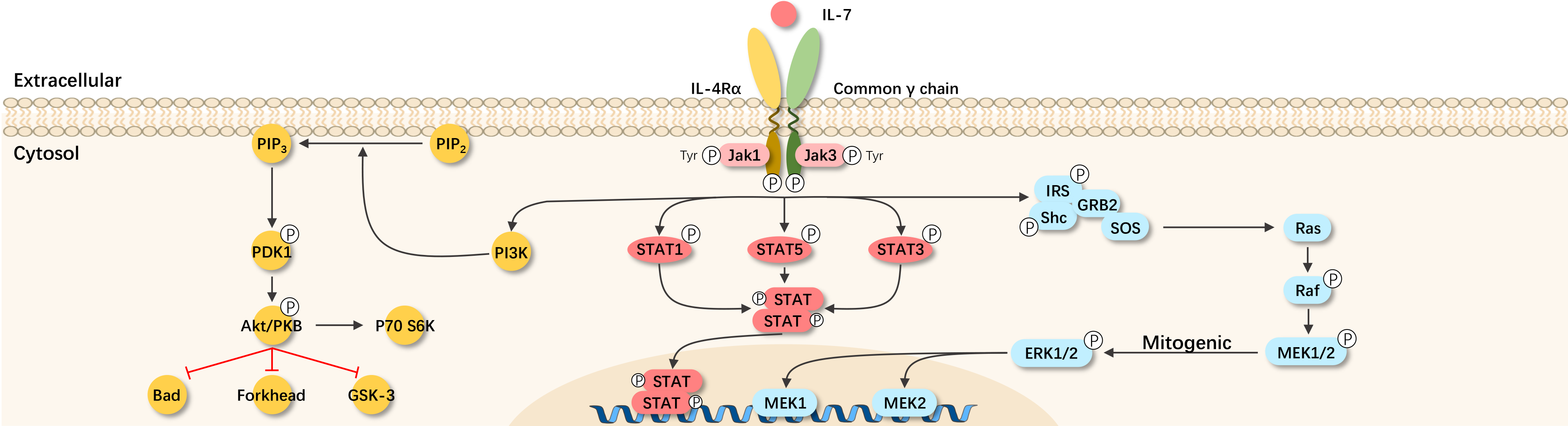
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) is a multifunctional cytokine with broad immunological effects. For a long time, the understanding of IL-7 has been linked to the growth, survival, and differentiation of B cells and T cells.
Research has shown that IL-7 expression is closely associated with T cell proliferation. Stimulation of fresh T cells with IL-7 results in dose-dependent expansion of T cells, including CD4+ and CD8+ subgroups; knocking out IL-7R halts T cell growth; introducing the IL-7 gene promotes the proliferation of CD4+/CD8+ T cells. However, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells respond differently to IL-7. IL-7 has a stronger effect on CD8+ T cell subgroups compared to CD4+ cell subgroups.
IL-7Rα is selectively expressed in a small subset of effector T cells during the initial immune response, then transforming into central memory T cells. IL-7 is particularly crucial for the survival of memory T cells. In lymphopenia, the role of IL-15 in memory T cells can be replaced by IL-7.
Due to IL-7's potent immunological effects, especially its role in regulating T cell proliferation, maintaining cellular homeostasis, and enhancing T cell immune responses, IL-7 is increasingly being recognized as an immune regulatory factor.