Overview of OX40/OX40L
The interaction between OX40 and its ligand OX40L plays a crucial role in the initiation and progression of inflammatory diseases, autoimmune disorders, cancer, and transplant immunity. In recent years, this area of research has gained increasing attention from scholars both in China and abroad.
OX40, also known as CD134, ACT35, or TNFRSF4, was first identified in 1987 on activated murine CD4+ T cells. It belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily. The OX40 gene is located on human chromosome 1, clustered together with several other TNFR family members, including TNFR2, 4-1BB, HVEM, CD30, GITR, and DR3.
OX40 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail. It contains three complete cysteine-rich domains (CRDs) and one partial C-terminal CRD.
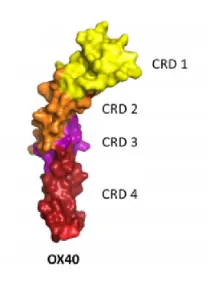
Figure 1. Structure of OX40, showing three complete CRDs and one truncated CRD.
OX40 is primarily expressed on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Upon binding to its ligand OX40L (also known as TNFSF4 or gp34), it can effectively enhance T cell proliferation and survival, thereby exerting a significant impact on immune responses to antigens and tumors.
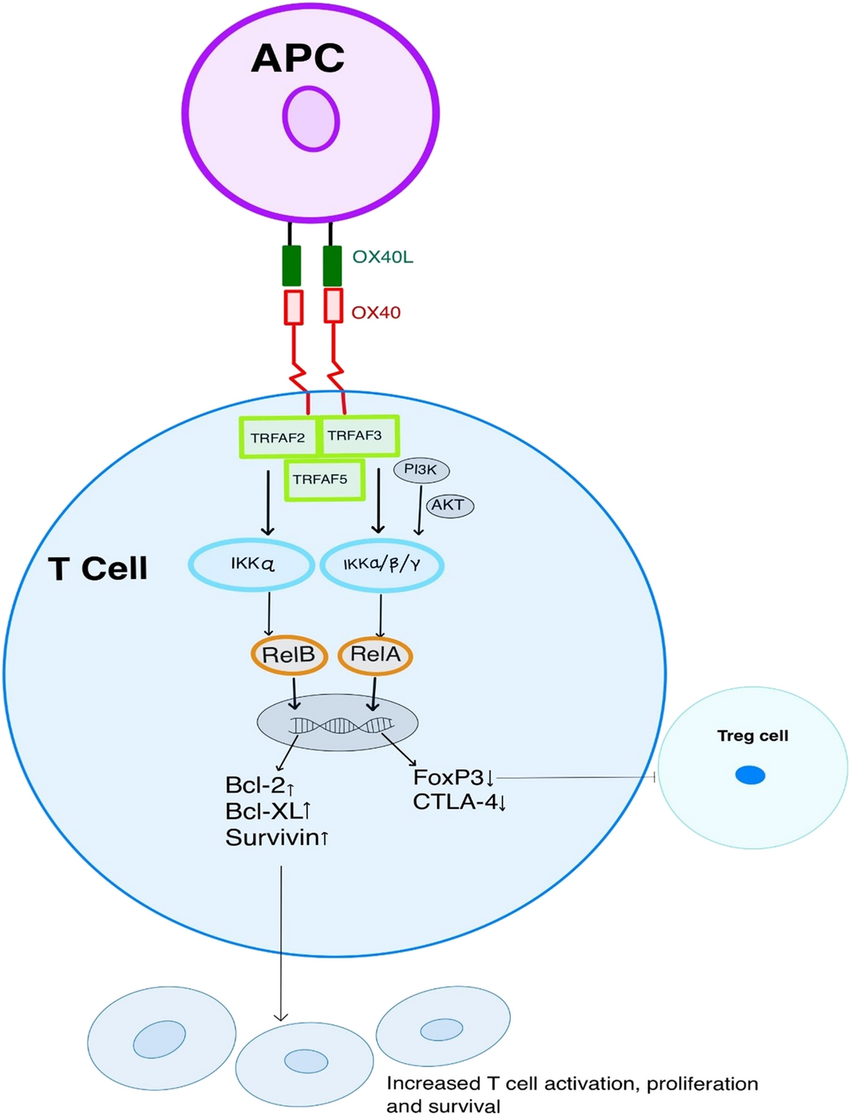
Figure 2. OX40/OX40Linteraction with downstream signaling results in T cell activation, proliferation, and increased survival.
OX40 expression on T cells is induced by signals such as TCR, CD28/CD80, and CD40/CD40L, reaching its peak 48–72 hours after T cell activation. TCR signaling initiates OX40 expression on various cell types, while CD28 and other cytokines further enhance its expression on activated T cells. Reports also indicate that cytokines such as IL-2, IL-4, and TNF can boost or prolong OX40 expression.
In a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) animal model, IL-2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ were highly expressed in liver tissue; however, only exogenous IL-2 stimulation was able to upregulate OX40 expression on CD4+ T cells.
OX40L is mainly expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and its expression can be detected within 1–3 days after APCs encounter antigens. CD40 signaling transmitted through Toll-like receptors, as well as inflammatory signals, can induce OX40L expression on APCs. Cytokines such as IL-18, IFN-γ, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), and prostaglandin E2 are also capable of promoting OX40L expression.
In addition to being expressed on professional APCs like activated B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), and macrophages, OX40L is also found on natural killer (NK) cells, mast cells, smooth muscle cells, and vascular endothelial cells.
OX40/OX40L Signaling Pathway
The biological function of the OX40–OX40L signaling pathway is to amplify the activation signal delivered to T cells by the T cell receptor (TCR).
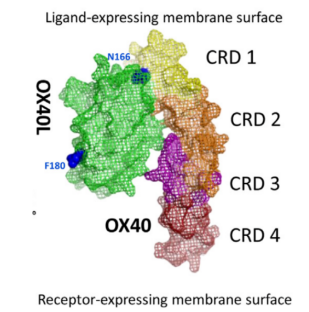
Figure 3. Model of OX40/OX40L Interaction
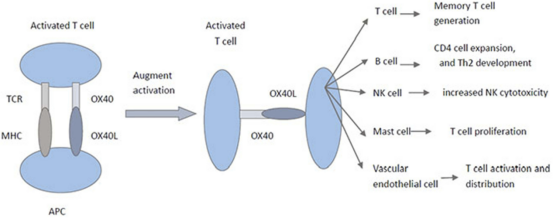
Abbreviations in figure: Th2 (T helper cell type 2), NK (Natural killer cell), TCR (T cell receptor), MHC (Major histocompatibility complex), APC (Antigen-presenting cell)
OX40L exists as a trimer, with each OX40L molecule binding to three OX40 receptors. The OX40/OX40L signaling can initiate downstream cascades through multiple pathways, including PI3K–PKB/AKT, nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), and NF-κB. Sustained activation of these pathways by OX40/OX40L signaling leads to the upregulation of certain anti-apoptotic members of the B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) family, such as Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and Bfl-1, as well as cell cycle regulators, thereby promoting cytokine production, T cell activation, and proliferation.
In addition, OX40/OX40L also mediates reverse signaling. This reverse signaling can regulate the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) in endothelial cells by modulating intracellular free calcium levels. Moreover, OX40/OX40L reverse signaling can promote the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs), activate B cells, and support the formation of germinal centers (GCs). These processes enhance the differentiation and maturation of DCs, enabling B cells to produce high-affinity antibodies and undergo class switching.
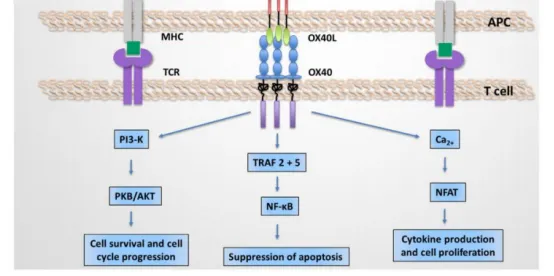
Figure 4. Downstream Signaling Pathways of OX40
OX40 in Disease Treatment
Role of OX40 in Cancer Therapy
OX40 signaling enhances T cell survival and immune activity, boosting tumor-specific T cell responses and memory formation. While monotherapy with OX40 agonists has shown limited efficacy, combination with other immunotherapies has significantly improved anti-tumor effects and is a major focus of current research.
Regulation of Autoimmunity and Inflammation
The OX40/OX40L pathway is actively involved in various autoimmune diseases. Blocking this pathway can mitigate excessive immune activation and has shown therapeutic potential in disease models such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and type 1 diabetes. Additionally, this pathway is closely associated with inflammatory conditions like atopic dermatitis, making it a valuable therapeutic target.
Progress in OX40-Targeted Drug Development
Several clinical trials targeting OX40 or OX40L in the field of autoimmunity are currently underway. Among the most advanced are Amgen/Kyowa Kirin’s Rocatinlimab (the first to successfully complete a Phase III study), Sanofi’s Amlitelimab (in Phase III), and Ichnos Sciences’ Telazorlimab (in Phase II). Other OX40/OX40L-targeted therapies, such as APG990 by Apogee Therapeutics, are in Phase I clinical trials.
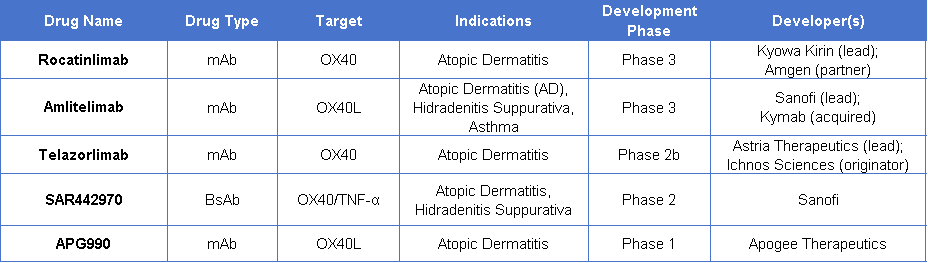
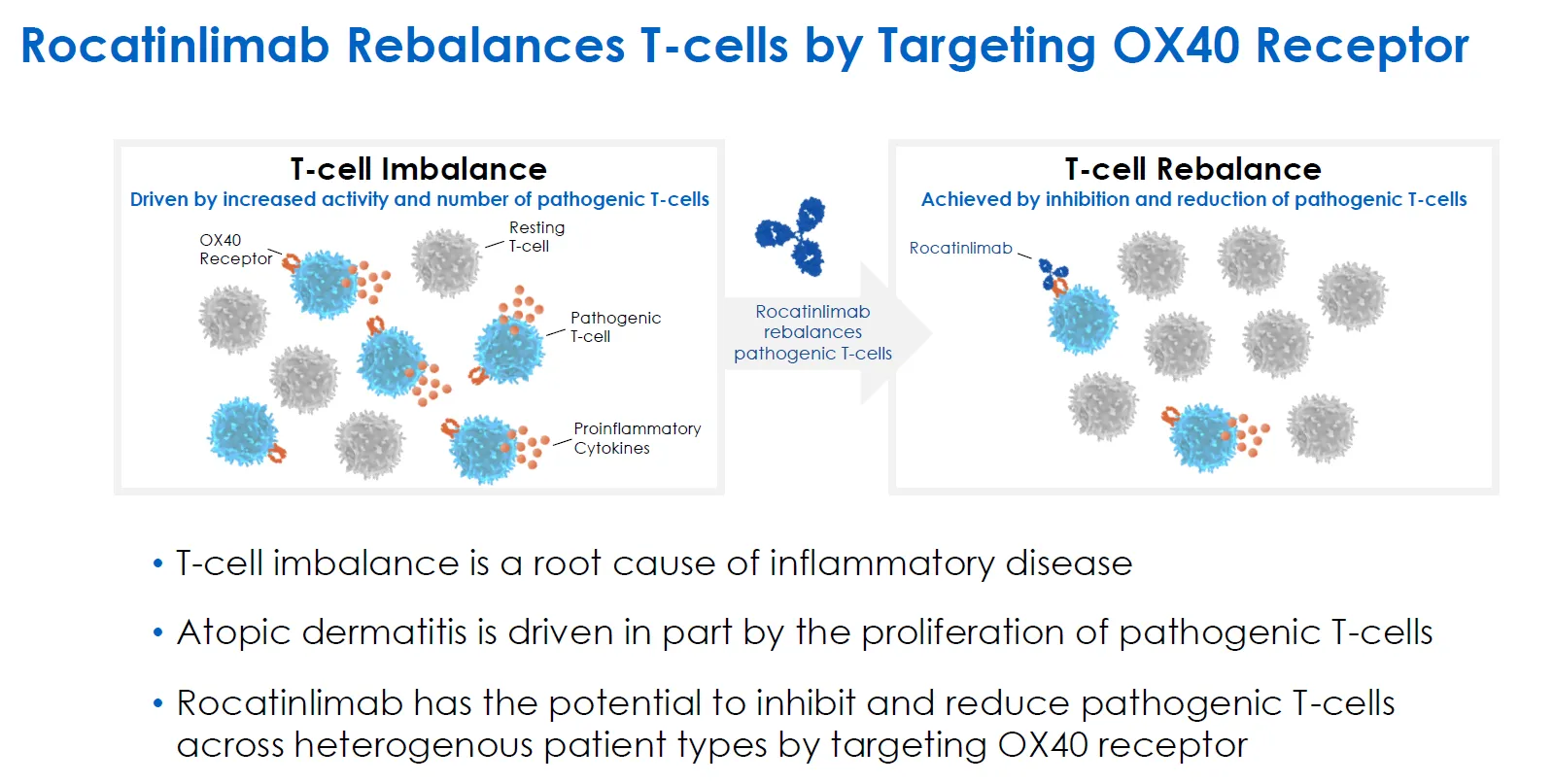
Rocatinlimab is a fully humanized, innovative anti-OX40 monoclonal antibody. Amgen entered a collaboration worth up to USD 1.25 billion with Kyowa Kirin to jointly develop and commercialize the drug. On March 8, 2025, Amgen and Kyowa Kirin jointly announced that Rocatinlimab met the primary endpoints in two Phase III clinical trials—ROCKET-IGNITE and ROCKET-SHUTTLE—for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
As the first anti-OX40 monoclonal antibody to successfully complete Phase III trials, Rocatinlimab has now delivered positive results in three consecutive Phase III studies. It is poised to become the first OX40-targeted antibody to gain global regulatory approval.
Amlitelimab is a fully human, non-depleting monoclonal antibody targeting OX40L, designed to block the OX40L–OX40 interaction. Compared to directly targeting OX40, it offers potential advantages in modulating immune responses with reduced risk of T cell overstimulation. The drug is currently in Phase IIb clinical development for atopic dermatitis and asthma.
On April 15, Sanofi announced that the Phase II TIDE-Asthma trial of Amlitelimab did not meet its primary endpoint of reducing the 48-week annualized exacerbation rate. However, the treatment showed compelling efficacy in a subgroup of patients with heterogeneous inflammatory asthma. Despite not achieving statistical significance overall, numerical reductions in exacerbations were observed through Week 60. Sanofi remains committed to advancing Amlitelimab into Phase III trials for asthma.
Summary
The rapid rise of OX40 as a therapeutic target marks a significant shift in autoimmune disease treatment—from traditional downstream pathway inhibition to upstream immune modulation. In the field of atopic dermatitis, both domestic and global pharmaceutical companies are positioning OX40-targeted therapies as strong contenders to challenge the IL-4Rα pathway, represented by dupilumab.
If OX40-targeting drugs can continue to demonstrate long-term safety and strong patient adherence, they have the potential to reshape the treatment paradigm and usher in a new era of autoimmune therapy—one that moves beyond reliance on IL-4Rα inhibition.
Reference
Amgen & Kyowa Kirin. (2025). Amgen and Kyowa Kirin Provide Top-Line Results from Rocatinlimab Phase 3 IGNITE Study in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Amgen. https://www.amgen.com/newsroom/press-releases/2025/03/amgen-and-kyowa-kirin-provide-top-line-results-from-rocatinlimab-phase-3-ignite-study-in-adults-with-moderate-to-severe-atopic-dermatitis?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Apogee Therapeutics, Inc. (2025). Apogee Therapeutics Announces Positive Interim Phase 1 Results from the APG990 Healthy Volunteer Trial, Unlocking Potential Maintenance Dosing Every Three and Six Months for APG279 (APG777 + APG990). https://investors.apogeetherapeutics.com/news-releases/news-release-details/apogee-therapeutics-announces-positive-interim-phase-1-results
Ichnos. (2023). ICHNOS Sciences enters licensing agreement for OX40 Antagonist Monoclonal Antibody portfolio with Astria Therapeutics. https://iginnovate.com/2024/01/16/ichnos-sciences-enters-licensing-agreement-for-ox40-antagonist-monoclonal-antibody-portfolio-with-astria-therapeutics/#
Sanofi. (2024). Press Release: New Phase 2b results for amlitelimab support potential for best-in-class maintenance of response in atopic dermatitis. https://www.sanofi.com/en/media-room/press-releases/2024/2024-03-11-06-00-00-2843456?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Sanofi. (2025). A study to test the efficacy and safety | Clinical Research Studies listing. https://www.sanofistudies.com/au/en/listing/312848/a-study-to-test-2/#original
Sanofi. (2025). Press Release: Sanofi’s respiratory pipeline advances with new data in asthma and plans for new clinical studies in COPD. https://www.sanofi.com/en/media-room/press-releases/2025/2025-04-15-05-00-00-306136