Overview of IL-17
Interleukin-17 (IL-17), also known as IL-17A, is the prototype of a relatively new six-member cytokine family. The IL-17 family includes six ligands (IL-17A to IL-17F) and five receptors (IL-17RA to IL-17RD and SEF).
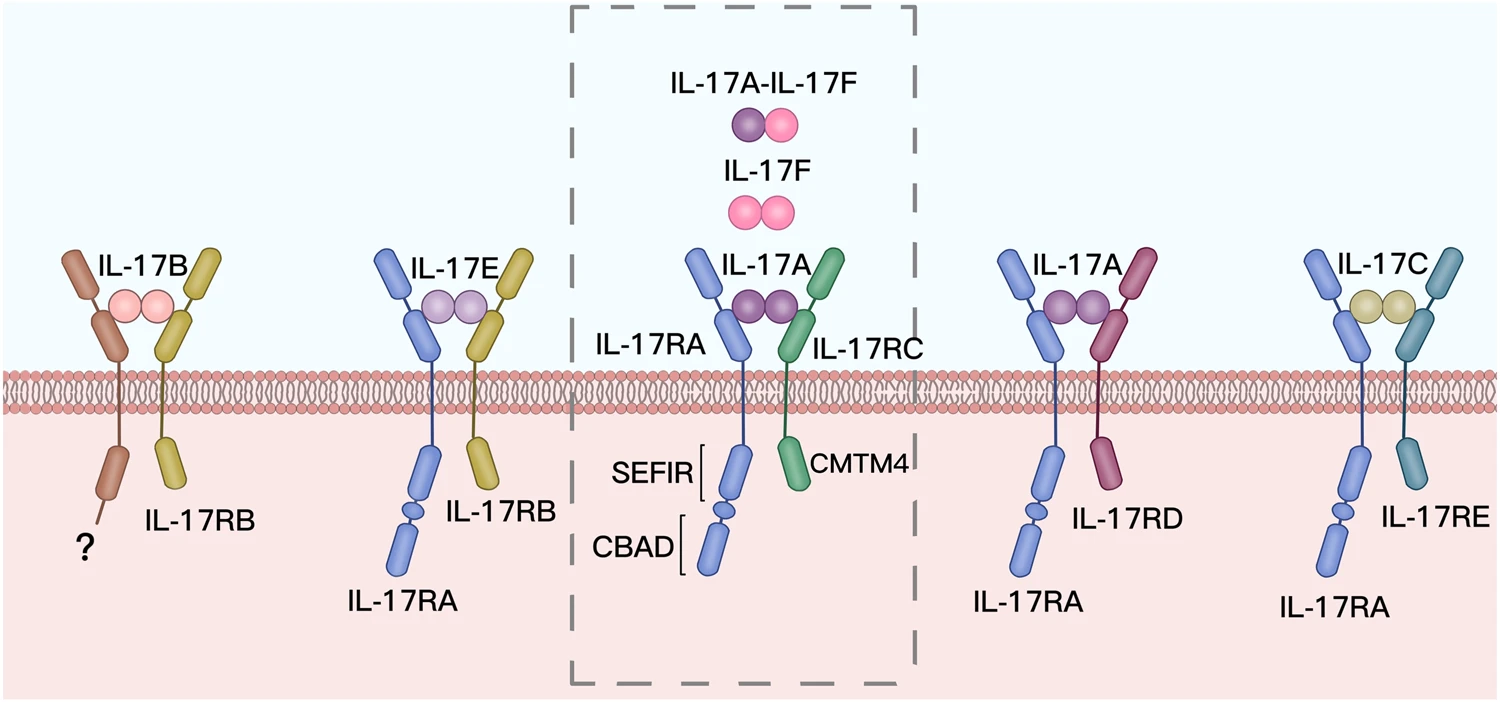
IL-17 Cytokine and Receptor Family
IL-17A and IL-17F, the most homologous members of the IL-17 cytokine family, drive similar pro-inflammatory pathways. As shown below, IL-17A can dimerize with IL-17F to activate downstream signaling via receptor complexes—making dual-targeting approaches a compelling therapeutic strategy.
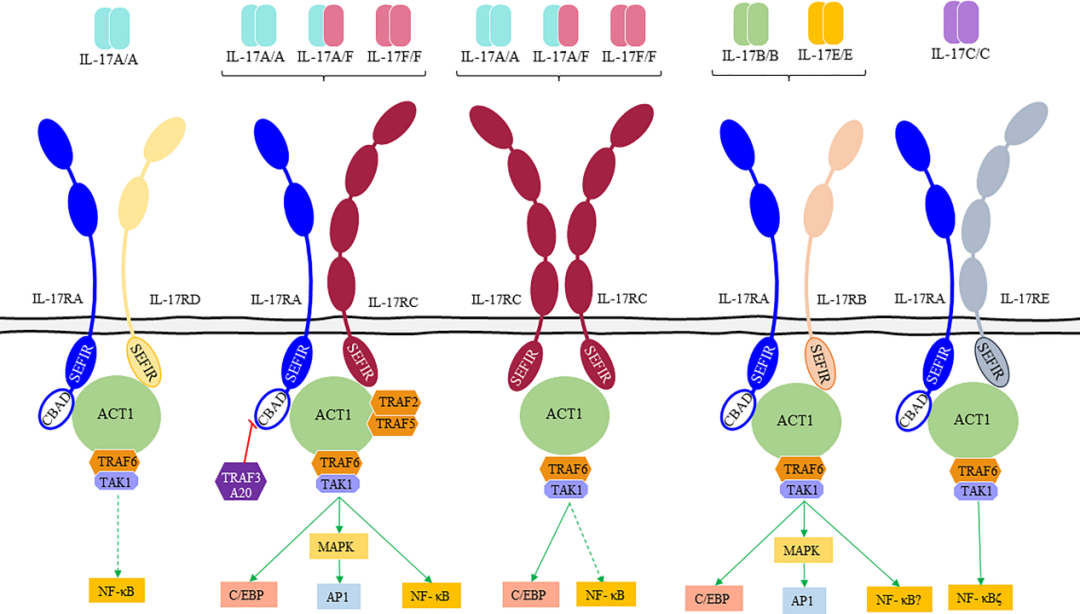
IL-17 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine primarily produced by activated T cells. It promotes the activation of T cells and stimulates epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts to secrete various cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), chemokines, and cellular adhesion molecule 1 (CAM-1), thereby triggering inflammatory responses.
When IL-17 binds to its receptor IL-17R, it activates downstream pathways involving ACT1 and NF-κB, which further promote the release of inflammatory factors like IL-6 and IL-8, ultimately initiating a cascade of inflammatory reactions.
Related Diseases
1. Psoriasis
Key target cells of IL-17A in psoriasis include keratinocytes, endothelial cells, and innate immune cells. A positive feedback loop exists in systemic inflammation: IL-17A secreted by Th17 cells stimulates keratinocytes to produce inflammatory factors, alters tissue-resident memory T cells (CD8⁺CD103⁺ TRM), and recruits activated lymphocytes to sustain chronic inflammation. Keratinocytes, in turn, secrete IL-17C, which activates Th17 cells to release more IL-17A, amplifying the inflammatory loop.
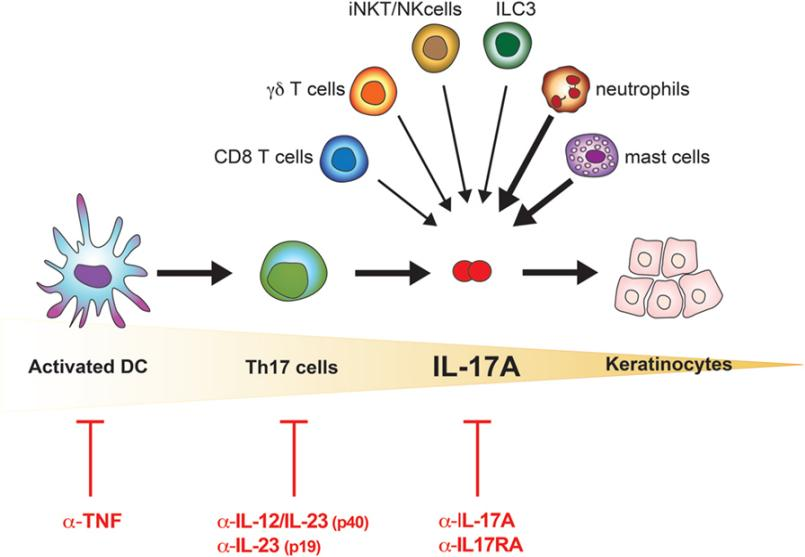
2. AS/PsA
Structural damage from chronic inflammation is a key factor in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In both conditions, IL-23/IL-17 axis activation promotes osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. IL-17 also regulates osteoblast activation and differentiation.
IL-23 stimulates Th17 cells to produce IL-17 and IL-22. IL-17 induces RANKL expression in osteoblasts, promoting osteoclast differentiation, and directly enhances osteoclastogenesis, resulting in bone erosion. IL-17 and IL-22 drive mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into osteoblasts and hypertrophic chondrocytes, causing new bone formation and eventually leading to spinal ankylosis.
3. Periodontitis
IL-17 regulates granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and C-X-C chemokines in fibroblasts, coordinating neutrophil production and recruitment to periodontal tissues. It suppresses the expression of Del-1 in endothelial cells, a glycoprotein that blocks neutrophil adhesion by interfering with LFA-1–ICAM-1 interaction. IL-17 also promotes matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and RANKL production in stromal cells, leading to connective tissue and bone destruction. Although IL-17 can induce antimicrobial peptides in epithelial cells, studies suggest its net effect promotes disease progression.
4. Cardiovascular Disease
In vitro studies show IL-17A acts on vascular components (endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, adipocytes) and cardiomyocytes, promoting cardiovascular inflammation. It induces endothelial cells to secrete inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Combined with IFN-γ, it induces chronic apoptosis in smooth muscle cells, accelerating atherosclerosis. In adipocytes, IL-17A increases pro-inflammatory factors and lipolysis, maintaining an inflammatory milieu. It also stimulates fibroblasts to increase collagen production, reduce vascular compliance, and contribute to hypertension.
Also in vivo, IL-17A plasma levels are elevated in patients with unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction and correlate with platelet aggregation, suggesting IL-17A may promote platelet aggregation in acute coronary syndromes. In atrial fibrillation models, elevated IL-17A levels correlate with inflammation and arrhythmia progression, and neutralizing IL-17A reduces atrial fibrillation incidence and duration.
A Competitive Global Landscape
Globally, six IL-17-targeting drugs have been approved:
Secukinumab (Novartis)
Ixekizumab (Eli Lilly)
Bimekizumab (UCB)
Netakimab (Biocad/Shanghai Pharma)
Seltuximab (Zhixiang Jintai)
Funakizumab (Hengrui)
Bimekizumab strongly and selectively neutralizes both IL-17A and IL-17F, whereas others only target IL-17A.
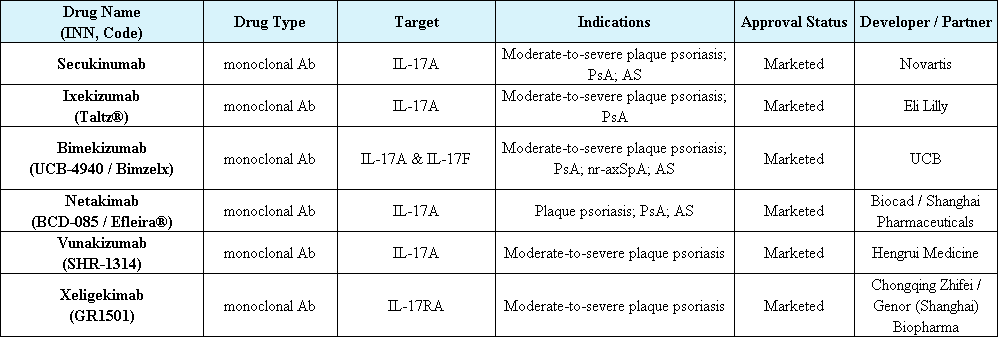
Secukinumab remains dominant in psoriasis treatment, generating over $6 billion globally in 2024. Despite launching in 2019, Eli Lilly’s Ixekizumab has struggled to gain traction. Bimekizumab, however, demonstrated superiority over Secukinumab in head-to-head trials and achieved rapid sales growth—rising from €148 million in 2023 to over €600 million in 2024. UCB expects peak sales to surpass €4 billion by 2030.
Conclusion
The IL-17 battlefront is defined by a contest of efficacy, pricing, innovation, and commercialization. While imported drugs have a head start, domestic players are pushing forward. The future belongs to those who can offer better clinical value, broader indications, and competitive pricing. For the innovative drug developers, the race is just beginning.
Reference
Eli Lilly. (2022). Lilly’s Taltz® (ixekizumab) Now Available in New, Citrate-Free Formulation to Reduce Injection Site Pain for Improved Patient Experience | Eli Lilly and Company. https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/lillys-taltzr-ixekizumab-now-available-new-citrate-free
Lane, I. (2025). Novartis’ Cosentyx GCA trial failure: a setback, but growth still ahead. Ainvest. https://www.ainvest.com/news/novartis-cosentyx-gca-trial-failure-setback-growth-2507/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
National Medical Products Administration. (2025). Vunakizumab injection approved for marketing by China NMPA. https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2025-02/19/c_1073596.htm?utm_source
National Medical Products Administration. (2024). Xeligekimab injection approved for marketing by China NMPA. https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2025-02/19/c_1073595.htm
Novartis. (2016). Novartis receives two new FDA approvals for Cosentyx® (secukinumab) to treat patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Novartis. https://www.novartis.com/us-en/news/media-releases/novartis-receives-two-new-fda-approvals-cosentyx-secukinumab-treat-patients-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Reichert, J. (2019). Anti-IL17 netakimab registered in Russia. The Antibody Society. https://www.antibodysociety.org/tag/netakimab/
UCB. (2024). UCB Announces U.S. FDA Approvals for BIMZELX® (bimekizumab-bkzx) for the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis, Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis. PR Newswire. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/ucb-announces-us-fda-approvals-for-bimzelx-bimekizumab-bkzx-for-the-treatment-of-psoriatic-arthritis-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-ankylosing-spondylitis-302255482.html
UCB. (2024). UCB on growth path for a decade plus. https://www.ucb.com/newsroom/press-releases/article/ucb-on-growth-path-for-a-decade-plus?utm_source