Cat. No:GM-032AS011
Product:H_CTLA4 CD80 Reporter Blockade Assay (CHO-aAPC)
Cat. No:GM-032AS011
Product:H_CTLA4 CD80 Reporter Blockade Assay (CHO-aAPC)

H_CTLA4 Reporter Jurkat Cell Line
Cell Growth Medium:RPMI 1640+10% FBS+1% P.S+3.5 μg/mL Blasticidin+0.75 μg/mL Puromycin
Cell Freezing Medium:90% FBS+10% DMSO
H_CD80 aAPC CHO-K1 Cell Line
Cell Growth Medium:F12K+10% FBS+1% P.S+4 μg/mL Puromycin+4 μg/mL Blasticidin
Cell Freezing Medium:90% FBS+10% DMSO
Assay Buffer:RPMI 1640+1% FBS+1% P.S
CTLA-4, also known as CD152, is an immunosuppressive receptor that is constitutively expressed on regulatory T cells (Treg). Plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. When CTLA4 is upregulated on the surface of T cells, T cells bind to CD80 (B7-1) or CD86 (B7-2) with higher affinity, surpassing the positive co stimulatory signal of CD28, thus inducing T cell unresponsiveness. Research has found that antibodies and Fc fusion proteins used to block the interaction between CTLA4/CD80 and CD86 have shown promising application prospects in clinical trials for the treatment of various cancers.
The current methods for measuring potential biological antibody activity targeting CTLA-4 rely on the measurement of primitive human T cells and functional end products, such as cell proliferation, cell surface marker expression, and production of interferon gamma (IFN gamma) and interleukin-2 (IL-2). Due to the reliance on donor primary cells, complex experimental protocols, and unqualified test reagents, these experiments are both laborious and variable. Therefore, these assay methods are difficult to establish in a quality controlled antibody development environment.
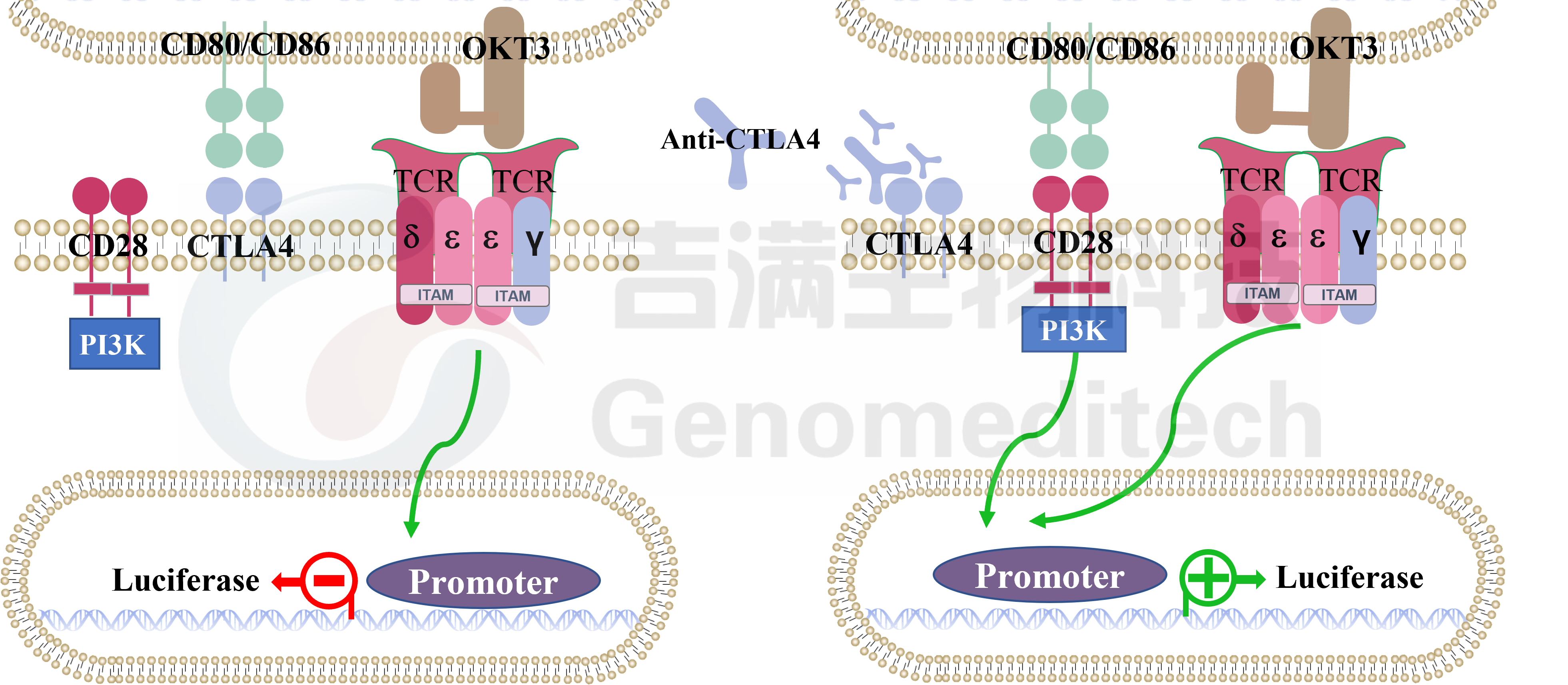
Jiman Biotech's H_CTLA4 CD80 Reporter Blockade Assay is a biologically relevant, mechanism of action (MOA) based detection method that can be used to determine the efficacy and stability of antibodies and other biological agents that block CTLA-4/CD80 interactions. This experiment consists of two genetically engineered cell lines:
CTLA4 effector cells refer to Jurkat T cells that stably express the human CTLA4 receptor and the luciferase reporter gene Jurkat in response to TCR/CD28 activation;
H_CD80 aAPC CHO-K1 Cell Line cells are a type of cell that stably expresses human CD80 and OKT3.
When two types of cells are co cultured, the interaction between CTLA4/CD80 inhibits the transduction of TCR signaling pathway and the expression of luciferase. After adding antibodies that block CTLA4, this inhibition will be released, causing the conduction of TCR signaling pathway and the expression of Luciferase.
Cat. No:GM-032AS011
Product:H_CTLA4 CD80 Reporter Blockade Assay (CHO-aAPC)

H_CTLA4 Reporter Jurkat Cell Line
Cell Growth Medium:RPMI 1640+10% FBS+1% P.S+3.5 μg/mL Blasticidin+0.75 μg/mL Puromycin
Cell Freezing Medium:90% FBS+10% DMSO
H_CD80 aAPC CHO-K1 Cell Line
Cell Growth Medium:F12K+10% FBS+1% P.S+4 μg/mL Puromycin+4 μg/mL Blasticidin
Cell Freezing Medium:90% FBS+10% DMSO
Assay Buffer:RPMI 1640+1% FBS+1% P.S
CTLA-4, also known as CD152, is an immunosuppressive receptor that is constitutively expressed on regulatory T cells (Treg). Plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses. When CTLA4 is upregulated on the surface of T cells, T cells bind to CD80 (B7-1) or CD86 (B7-2) with higher affinity, surpassing the positive co stimulatory signal of CD28, thus inducing T cell unresponsiveness. Research has found that antibodies and Fc fusion proteins used to block the interaction between CTLA4/CD80 and CD86 have shown promising application prospects in clinical trials for the treatment of various cancers.
The current methods for measuring potential biological antibody activity targeting CTLA-4 rely on the measurement of primitive human T cells and functional end products, such as cell proliferation, cell surface marker expression, and production of interferon gamma (IFN gamma) and interleukin-2 (IL-2). Due to the reliance on donor primary cells, complex experimental protocols, and unqualified test reagents, these experiments are both laborious and variable. Therefore, these assay methods are difficult to establish in a quality controlled antibody development environment.
Jiman Biotech's H_CTLA4 CD80 Reporter Blockade Assay is a biologically relevant, mechanism of action (MOA) based detection method that can be used to determine the efficacy and stability of antibodies and other biological agents that block CTLA-4/CD80 interactions. This experiment consists of two genetically engineered cell lines:
CTLA4 effector cells refer to Jurkat T cells that stably express the human CTLA4 receptor and the luciferase reporter gene Jurkat in response to TCR/CD28 activation;
H_CD80 aAPC CHO-K1 Cell Line cells are a type of cell that stably expresses human CD80 and OKT3.
When two types of cells are co cultured, the interaction between CTLA4/CD80 inhibits the transduction of TCR signaling pathway and the expression of luciferase. After adding antibodies that block CTLA4, this inhibition will be released, causing the conduction of TCR signaling pathway and the expression of Luciferase.