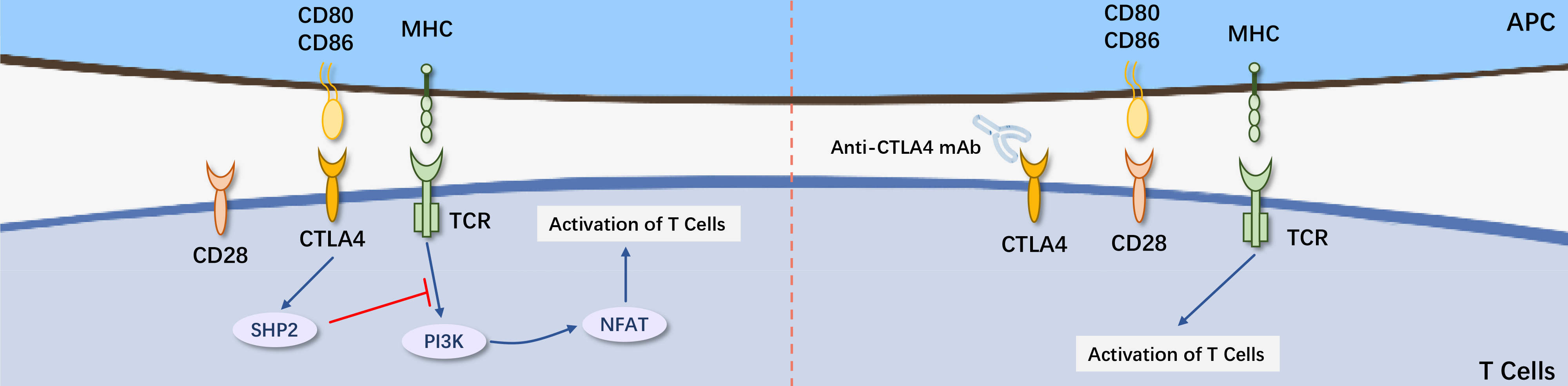
CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, also known as CD152) is a member of the immunoglobulin family. CTLA-4 is expressed on the surface of activated T cells, homologous to CD28 (T cell co-stimulatory factor). Both can bind to CD80 and CD86 on antigen-presenting cells' surfaces (also known as B7-1 and B7-2). CD28 is responsible for delivering activation signals, activating T cells; while CTLA-4 delivers inhibitory signals to T cells, preventing them from killing other cells, including tumor cells. Moreover, CTLA-4 has a much higher affinity for CD80 and CD86, thereby competing with and blocking the activating effect of CD28.
In resting naive T cells, CTLA-4 is primarily located intracellularly. The stimulus signals generated by TCR and CD28:B7 induce CTLA-4 to translocate to the cell surface through exocytosis of vesicles containing CTLA-4. Negative regulatory signals are produced through competitive binding of CTLA-4:B7, inhibiting IL-2 production and cell cycle progression to prevent complete activation of T cells.
Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies can restore T cell activation signals, enhance T cell activation and proliferation, restore the immune system's ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, exerting anti-tumor effects through T cell-mediated immune responses. It can also modulate regulatory T cells' suppression through Fcγ receptor-dependent mechanisms, thereby increasing the proportion of effector T cells, reversing the immunosuppressive state of T cells, and enhancing the body's anti-tumor capabilities.