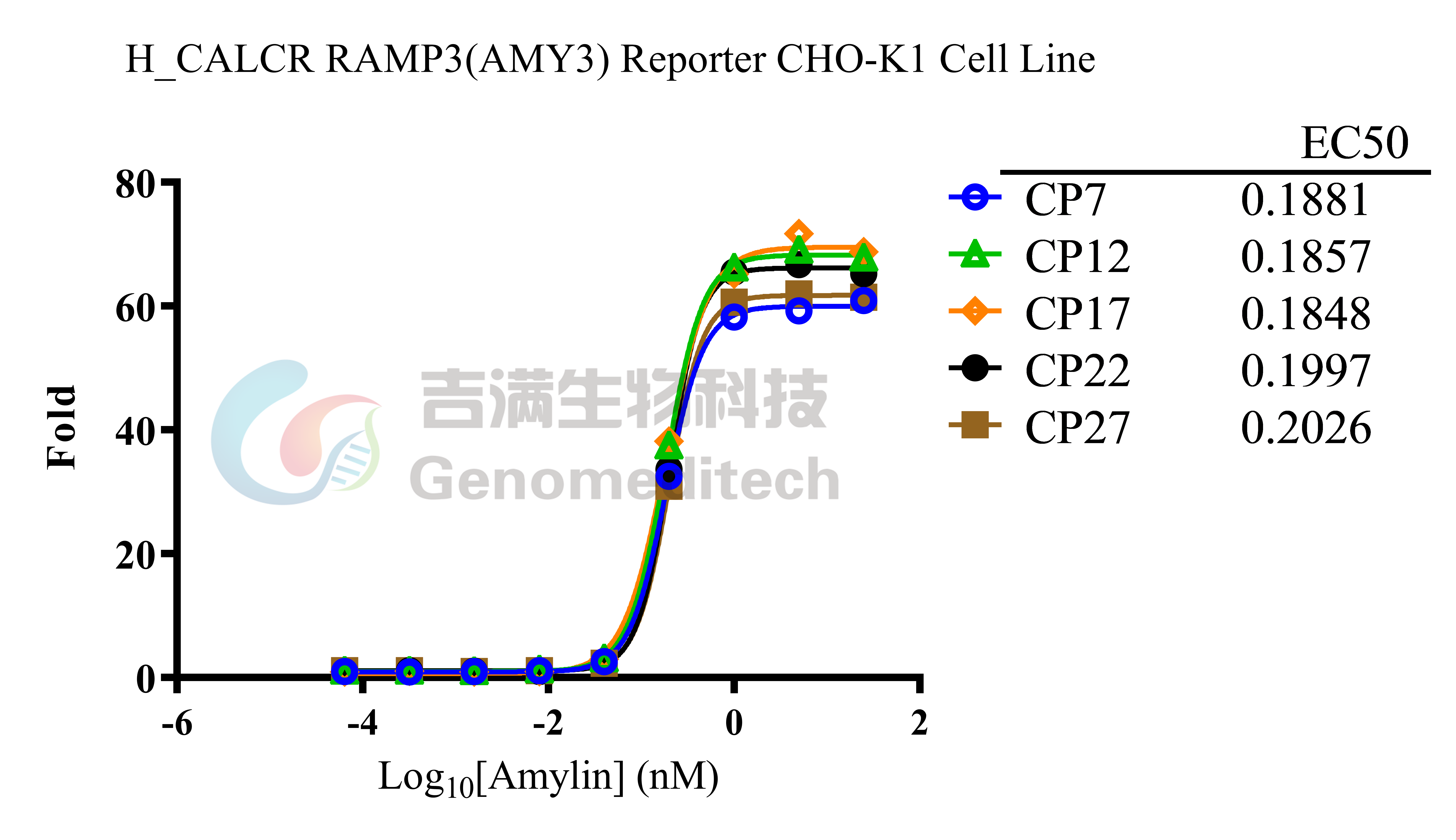
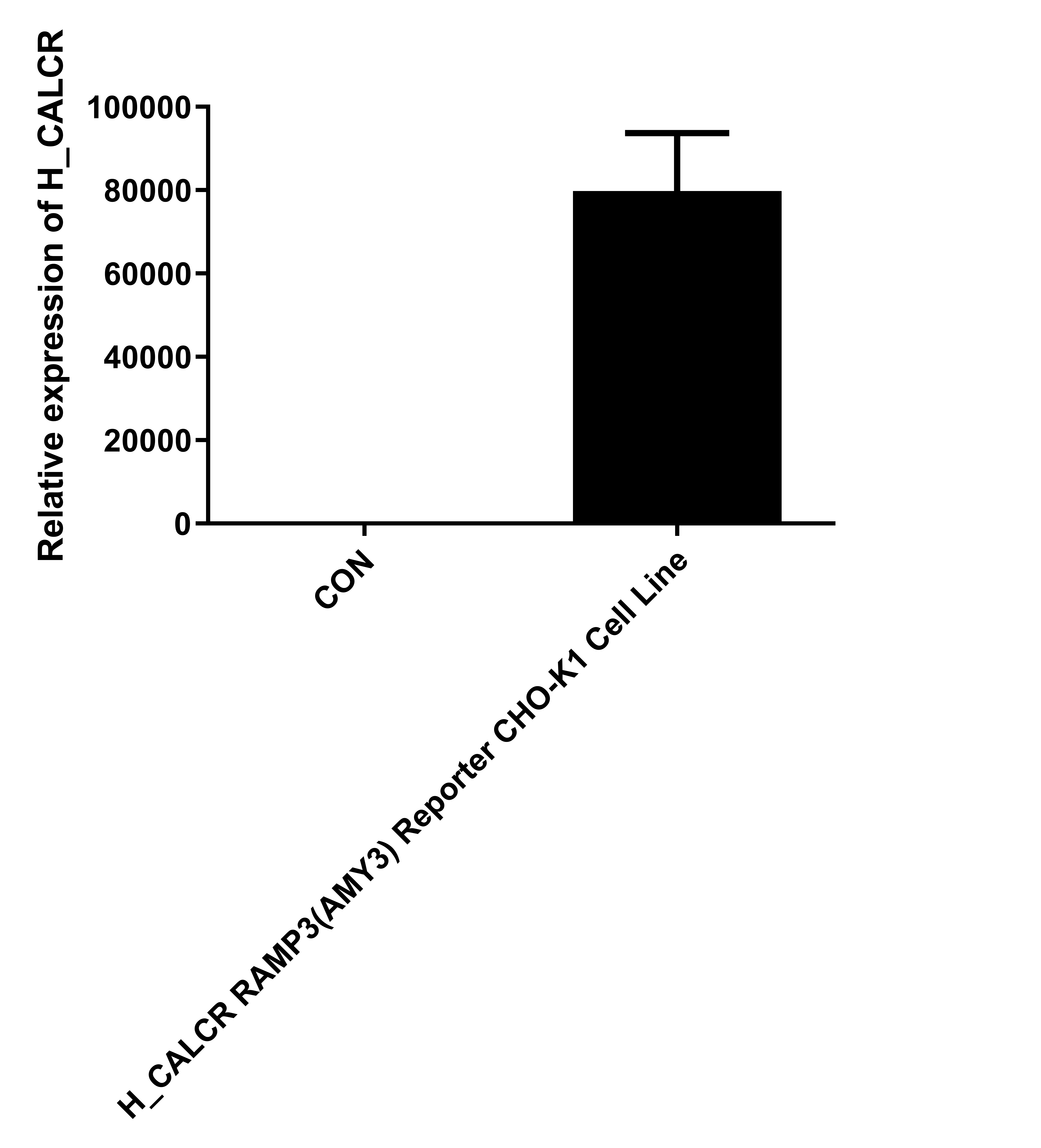
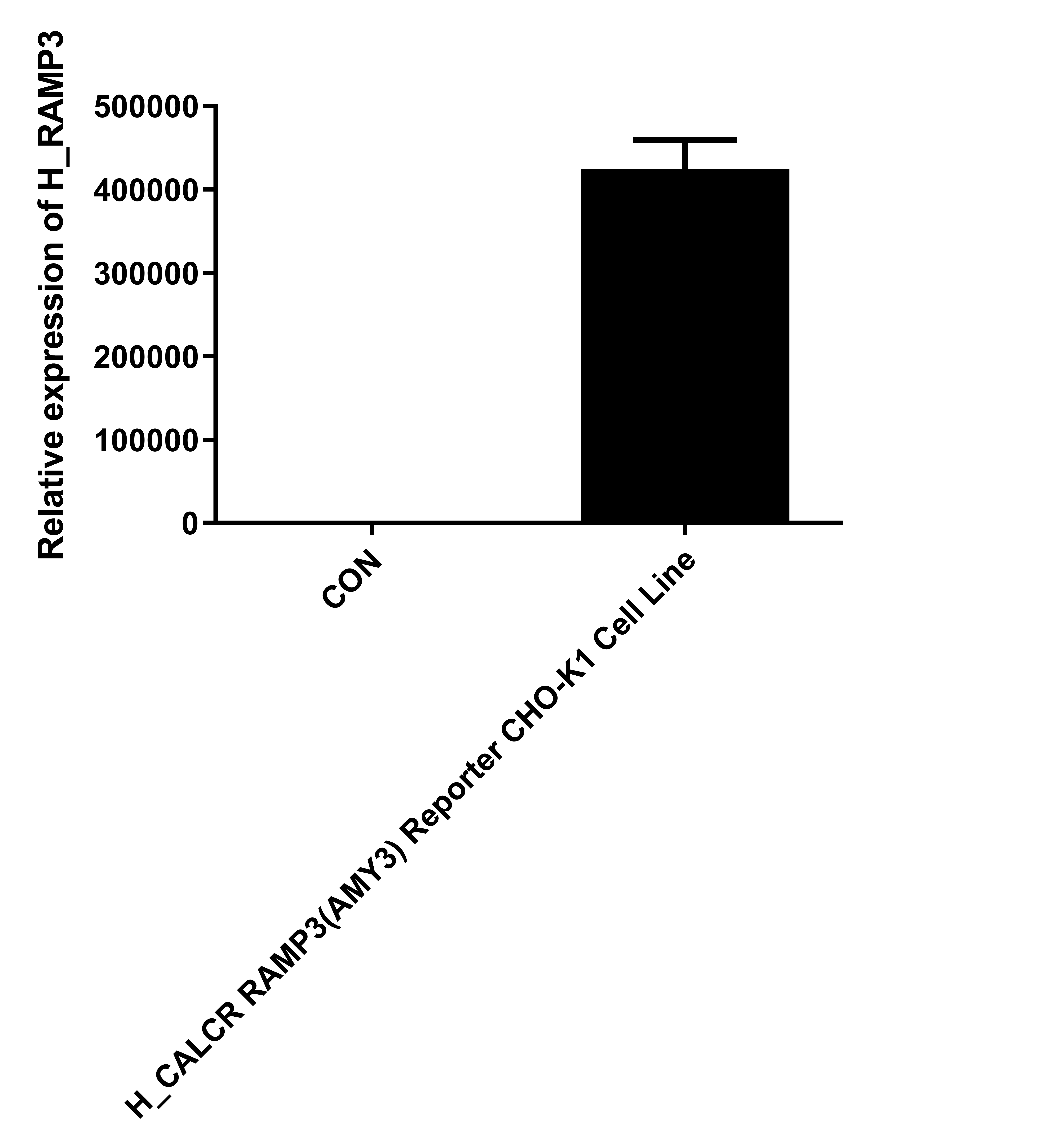
| Cat. No: GM-C26533 Product: H_CALCR RAMP3(AMY3) Reporter CHO-K1 Cell Line The Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (CGRP) family includes several important peptides: Calcitonin (CT), Amylin, and Adrenomedullin (AM). Amylin is produced by the pancreas and is a hormone that regulates nutrient intake. The binding of Amylin to its receptors involves three classes of potential receptors, which are complexes of the Calcitonin Receptor (CALCR) and Receptor Activity Modifying Proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are a series of type I single-transmembrane proteins that function by forming heterodimers with G protein-coupled receptors. There are three RAMP subtypes: RAMP1, RAMP2, and RAMP3. Although these RAMPs are structurally similar, their amino acid sequences are only about30% identical. After binding to the receptor, Amylin can form different complexes: CALCR combined with RAMP1 forms the Amy1 complex, CALCR combined with RAMP2 forms the Amy2 complex, and CALCR combined with RAMP3 forms the Amy3 complex. The H_CALCR RAMP3 (AMY3) Reporter CHO-K1 Cell Line is a clonal, stable cell line that constitutively expresses human CALCR and human RAMP3, along with a signal-dependent expression of a luciferase reporter gene. The binding of Amylin to the receptor complex activates downstream reporter genes, leading to luciferase expression. The luciferase readout indicates the activation level of the signaling pathway and can thus be used to evaluate the in vitro effects of drugs related to the CALCR RAMP3 (AMY3) complex. | 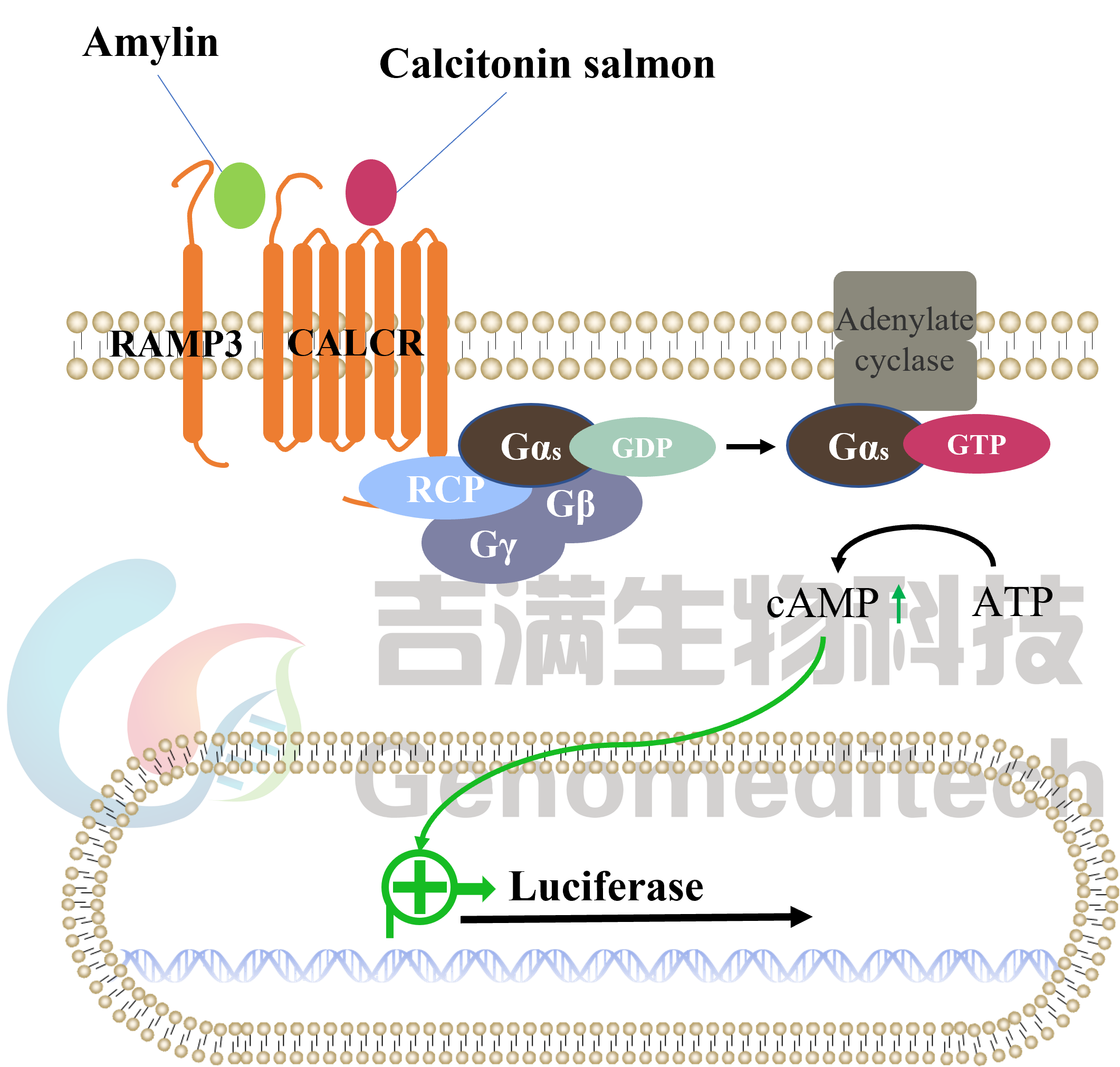 |