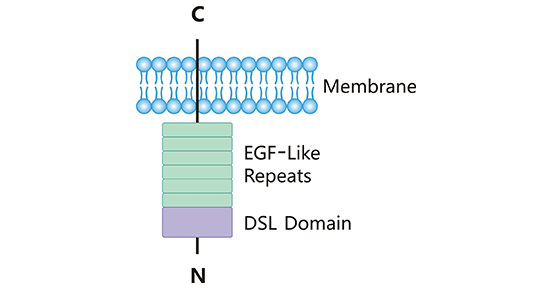
DLL3 is a single-pass transmembrane protein that belongs to the Notch ligand family. The human DLL3 protein consists of 619 amino acids, with a complete structure comprising one DSL domain, one intracellular domain, and six EGF-like domains.
The Notch signaling pathway is involved in various biological processes, such as cell proliferation, malignant transformation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Unlike other Notch ligands, DLL3 is an inhibitory Notch ligand. When DLL3 binds to the Notch receptor, it exerts an inhibitory effect on the Notch signaling pathway.
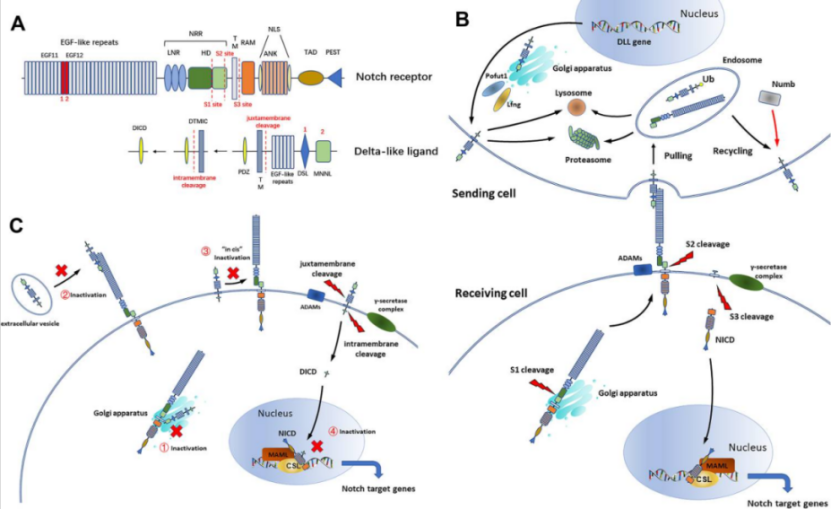
In small cell lung cancer (SCLC), DLL3 expression is particularly pronounced. High levels of DLL3 can be detected in approximately 85%–96% of SCLC tumor tissues, while it is nearly absent in normal adult tissues, with only limited expression during embryonic neural development. This tumor-specific high expression and low normal tissue expression pattern make DLL3 not only an important biomarker for SCLC but also an ideal target for drug development.
DLL3 Target Drug Development Landscape
The development of DLL3-targeted therapies has been a rollercoaster. As early as 2016, AbbVie recognized DLL3’s potential and acquired Stemcentrx for a hefty $5.8 billion in cash and stock, plus up to $4 billion in milestone payments, securing the DLL3-targeted ADC Rova-T. However, Rova-T failed to meet clinical expectations, and by the end of 2018, AbbVie had to halt patient recruitment for the Phase III TAHOE study, plunging the DLL3 field into a period of stagnation.
The failure of Rova-T temporarily dampened DLL3 development, but hope was renewed with Amgen’s Tarlatamab. Tarlatamab precisely directs T cells to DLL3-positive tumor cells, achieving targeted killing, and has demonstrated durable and controllable anticancer effects in clinical trials. Today, DLL3 research is advancing rapidly worldwide, with strategies including bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and CAR-T/CAR-NK immunotherapies, offering new hope for precise treatment of SCLC and other neuroendocrine tumors.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
ADCs are the most common type in the DLL3-targeted therapy pipeline, with multiple candidates in clinical trials for solid tumors and advanced malignancies. These next-generation ADCs use cytotoxic payloads, such as topoisomerase inhibitors, linked to DLL3-specific antibodies. The antibodies bind selectively to DLL3-expressing tumor cells, triggering internalization of the payload, inducing apoptosis, and achieving precise tumor cell killing.
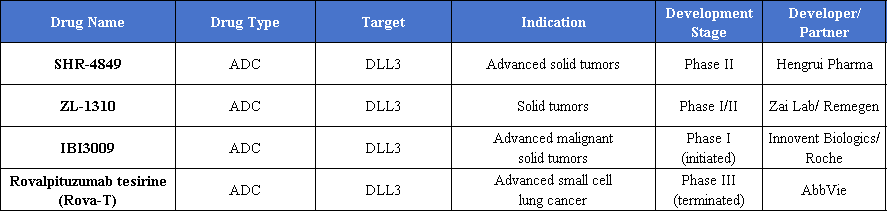
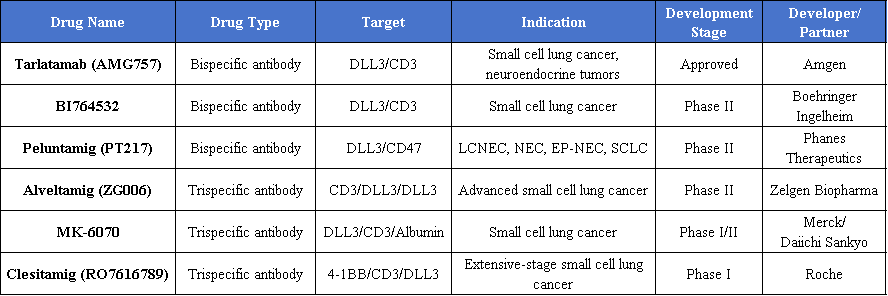
n clinical development, Hengrui’s SHR-4849 has entered Phase II. Phase I data showed that among 11 evaluable SCLC patients, 8 achieved partial responses, yielding an overall response rate of 73%, with manageable safety. Zai Lab’s ZL-1310 is in Phase I/II and has received FDA Fast Track designation for SCLC. Its DLL3-targeting antibody is conjugated with a novel camptothecin derivative, potentially overcoming the off-target toxicity of first-generation ADCs and showing significant promise.
On the business side, DLL3-related assets have demonstrated substantial value. Innovent announced on January 2 a global exclusive collaboration with Roche to develop IBI3009, including an upfront payment of $80 million and up to $1 billion in milestone payments. Hengrui licensed global rights (excluding Greater China) of SHR-4849 to U.S.-based IDEAYA in December 2024, with a potential total deal value of $1.045 billion. These developments highlight the strategic importance of DLL3 assets in international collaborations.
Bispecific and Trispecific Antibodies
Tarlatamab (AMG 757) is a first-in-class bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) targeting DLL3 and CD3. As a BiTE, Tarlatamab recruits T cells to the vicinity of small cell lung cancer cells, activating them to kill the tumor cells.
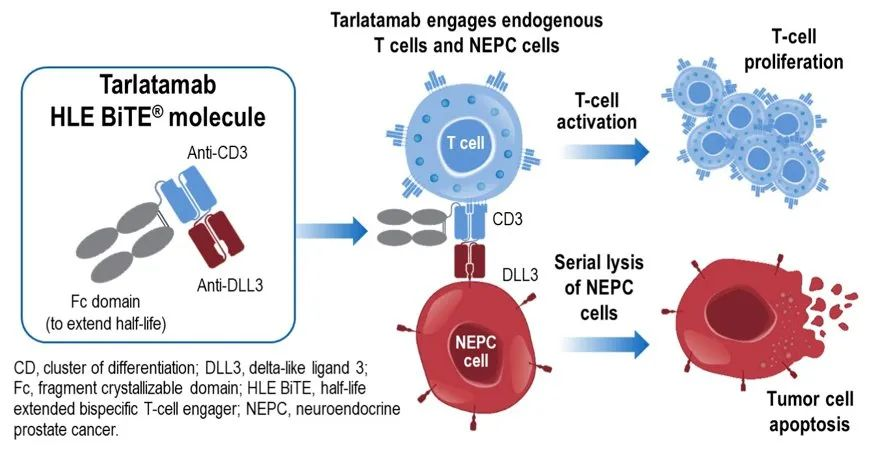
Tarlatamab’s approval was based on results from the Phase II DeLLphi-301 study. In Phase I/II trials, Tarlatamab demonstrated durable anticancer activity and manageable safety in patients with previously treated small cell lung cancer.
In May 2024, Amgen’s bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) Tarlatamab received FDA accelerated approval for the treatment of adult patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) who have progressed during or after chemotherapy. Notably, Tarlatamab is the first DLL3-targeting bispecific T-cell engager approved for treating aggressive lung cancer.
In July 2025, BeiGene, in collaboration with Amgen, submitted a marketing application in China for adult patients with ES-SCLC who have failed at least two prior lines of therapy, and the application was granted priority review. In August, BeiGene and Royalty Pharma finalized a royalty deal with an upfront payment of $885 million, covering most DLL3/CD3 bispecific revenues outside China, highlighting the substantial commercial value of DLL3 as a target.
In the trispecific antibody field, Zegene’s ZG006 (DLL3×CD3 trispecific T-cell engager) is being developed as a Breakthrough Therapy for advanced SCLC. Phase II data show an overall response rate (ORR) of 62.5% with favorable safety.
Cellular Therapies
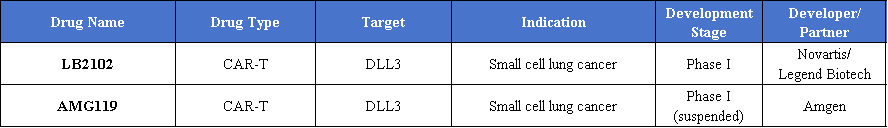
CAR-T therapies targeting DLL3 are being actively investigated for small cell lung cancer. Notable candidates in early clinical development include LB2102, a DLL3-directed CAR-T in Phase I trials developed by Novartis and Legend Biotech, and AMG119, another DLL3-targeted CAR-T developed by Amgen, currently in Phase I but temporarily suspended. LB2102 has demonstrated good tolerability and preliminary antitumor activity, with no dose-limiting toxicities or neurotoxicity reported in dose-escalation studies.
Conclusion
DLL3-targeted therapies are transitioning from a research hotspot to clinical practice, characterized by both global competition and collaboration. Although Amgen’s Tarlatamab was the first approved therapy, clinical limitations remain, leaving opportunities for later entrants to differentiate through improved efficacy, safety, and dosing convenience. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains the primary initial indication, with intense competition, while the neuroendocrine tumor space is comparatively less crowded.
The global DLL3 pipeline spans bispecific, trispecific, ADC, CAR-T, and CAR-NK modalities, with particularly strong potential in ADCs and cellular therapies. As more therapies gain approval and advance through clinical trials, DLL3-targeted approaches are expected to provide survival benefits for SCLC patients while offering strategic and investment opportunities for pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
Reference
AbbVie. (2019, August 29). AbbVie discontinues Rovalpituzumab Tesirine (Rova-T) research and development program [Press release]. AbbVie News.
https://news.abbvie.com/2019-08-29-AbbVie-Discontinues-Rovalpituzumab-Tesirine-Rova-T-Research-and-Development-Program
Amgen. (2024, May). FDA approves Imdelltra (tarlatamab-dlle), the first and only T-cell engager therapy for the treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer [Press release]. Amgen Newsroom.
https://www.amgen.com/newsroom/press-releases/2024/05/fda-approves-imdelltra-tarlatamabdlle-the-first-and-only-tcell-engager-therapy-for-the-treatment-of-extensivestage-small-cell-lung-cancer
Boehringer Ingelheim. (n.d.). Obrixtamig (BI 764532): DLL3/CD3 T-cell engager [Clinical pipeline]. Boehringer Ingelheim.
https://www.boehringer-ingelheim.com/science-innovation/human-health-innovation/clinical-pipeline/obrixtamig-bi-764532-dll3-cd3-t-cell-engager
ClinicalTrials.gov. (2023). Study of PT217 in patients with neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NCT06283719). U.S. National Library of Medicine.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06283719
ClinicalTrials.gov. (2022). Study of OSE-127 (NCT05619744). U.S. National Library of Medicine.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05619744
FierceBiotech. (2023). Roche returns to Innovent Biologics with new $1B biobucks ADC drug deal. FierceBiotech.
https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/roche-returns-innovent-biologics-new-1b-biobucks-adc-drug-deal
IDEAYA Biosciences, & Hengrui Pharmaceuticals. (2025). Oral presentation at IASLC 2025 World Conference on Lung Cancer for IDE849/SHR-4849, a potential first-in-class DLL3-TOP1 ADC [Press release]. PR Newswire.
https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/ideaya-biosciences-and-hengrui-pharmaceuticals-announce-oral-presentation-at-iaslc-2025-world-conference-on-lung-cancer-for-ide849-shr-4849-a-potential-first-in-class-dll3-top1-adc-302510323.html
Legend Biotech. (2024). Legend Biotech announces FDA clearance of IND application for LB2102 [Press release]. Legend Biotech Investors.
https://investors.legendbiotech.com/news-releases/news-release-details/legend-biotech-announces-fda-clearance-ind-application-lb2102
Merck, & Daiichi Sankyo. (2023). Daiichi Sankyo and Merck enter into global development and commercialization agreement for MK-6070 [Press release]. Merck News.
https://www.merck.com/news/daiichi-sankyo-and-merck-enter-into-global-development-and-commercialization-agreement-for-mk-6070/
OncLive. (2024). FDA grants fast track designation to PT217 for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. OncLive.
https://www.onclive.com/view/fda-grants-fast-track-designation-to-pt217-for-neuroendocrine-prostate-cancer
Pharmaceutical Technology. (2024). AMG 119 by Amgen for small cell lung cancer: Likelihood of approval. Pharmaceutical Technology.
https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/data-insights/amg-119-amgen-small-cell-lung-cancer-likelihood-of-approval/
Steinbuck, M. P., & Winandy, S. (2018). A Review of Notch Processing With New Insights Into Ligand-Independent Notch Signaling in T-Cells. Frontiers in immunology, 9, 1230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01230
Zai Lab. (2024). Zai Lab receives US FDA fast track designation for ZL-1310 (DLL3) [Press release]. Zai Lab News.
https://zailab.gcs-web.com/news-releases/news-release-details/zai-lab-receives-us-fda-fast-track-designation-zl-1310-dll3