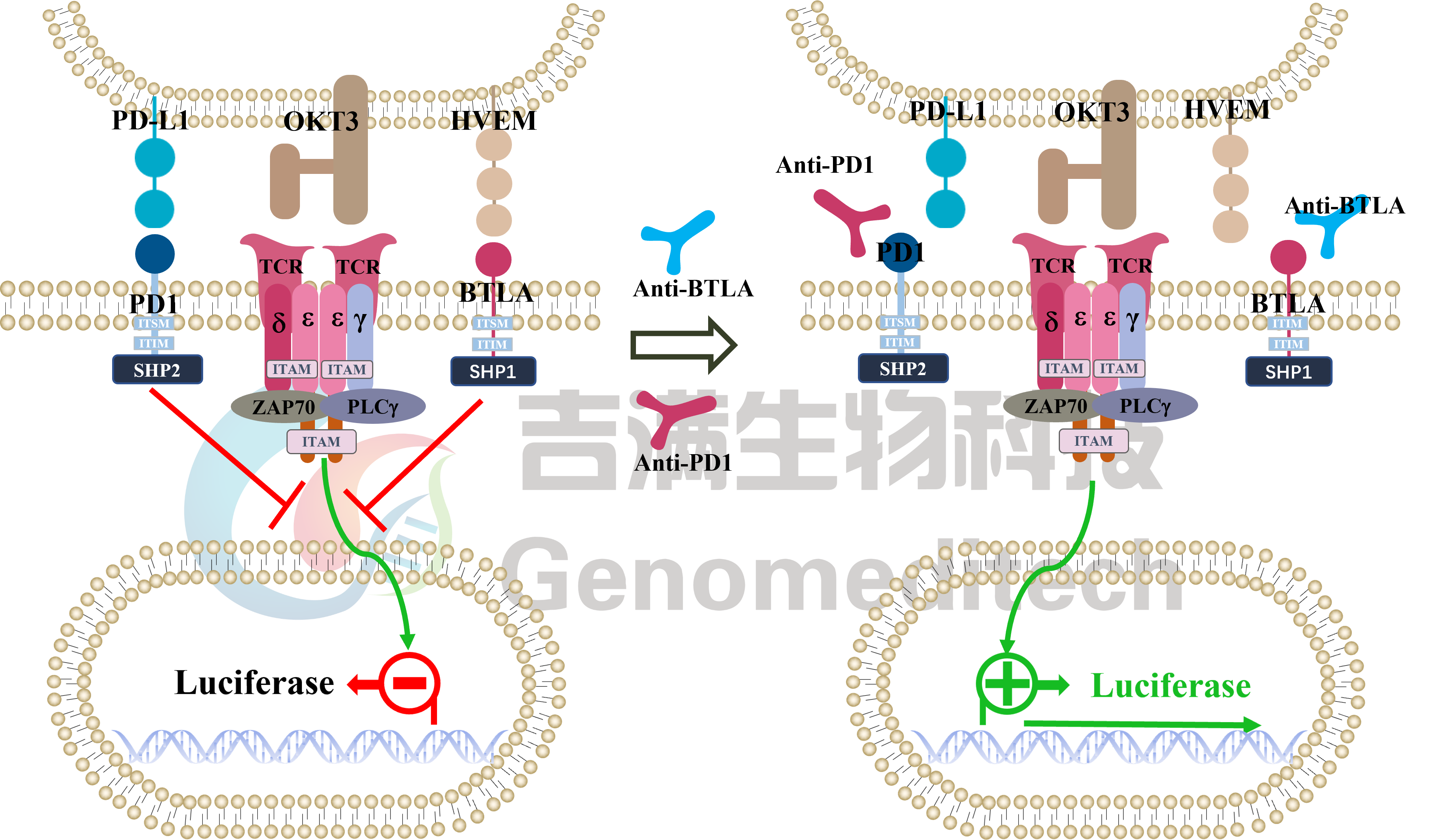
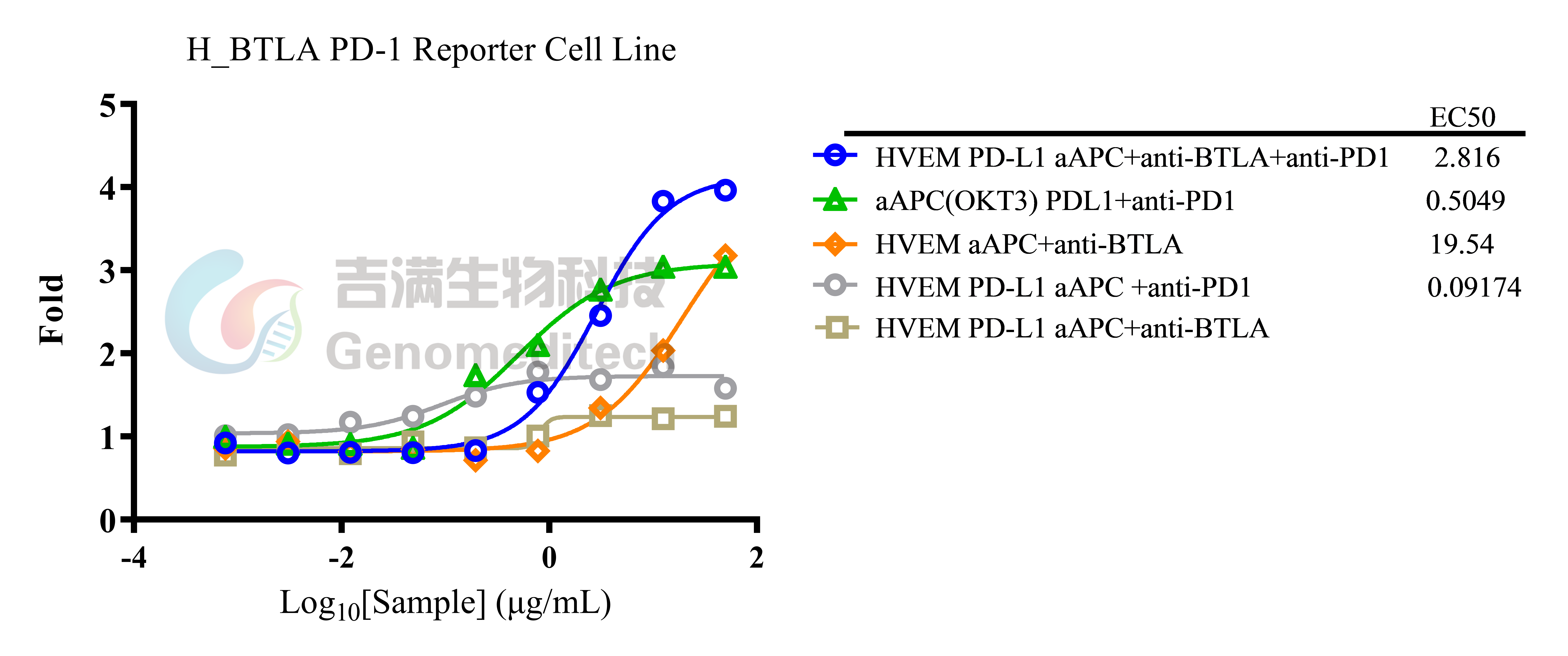
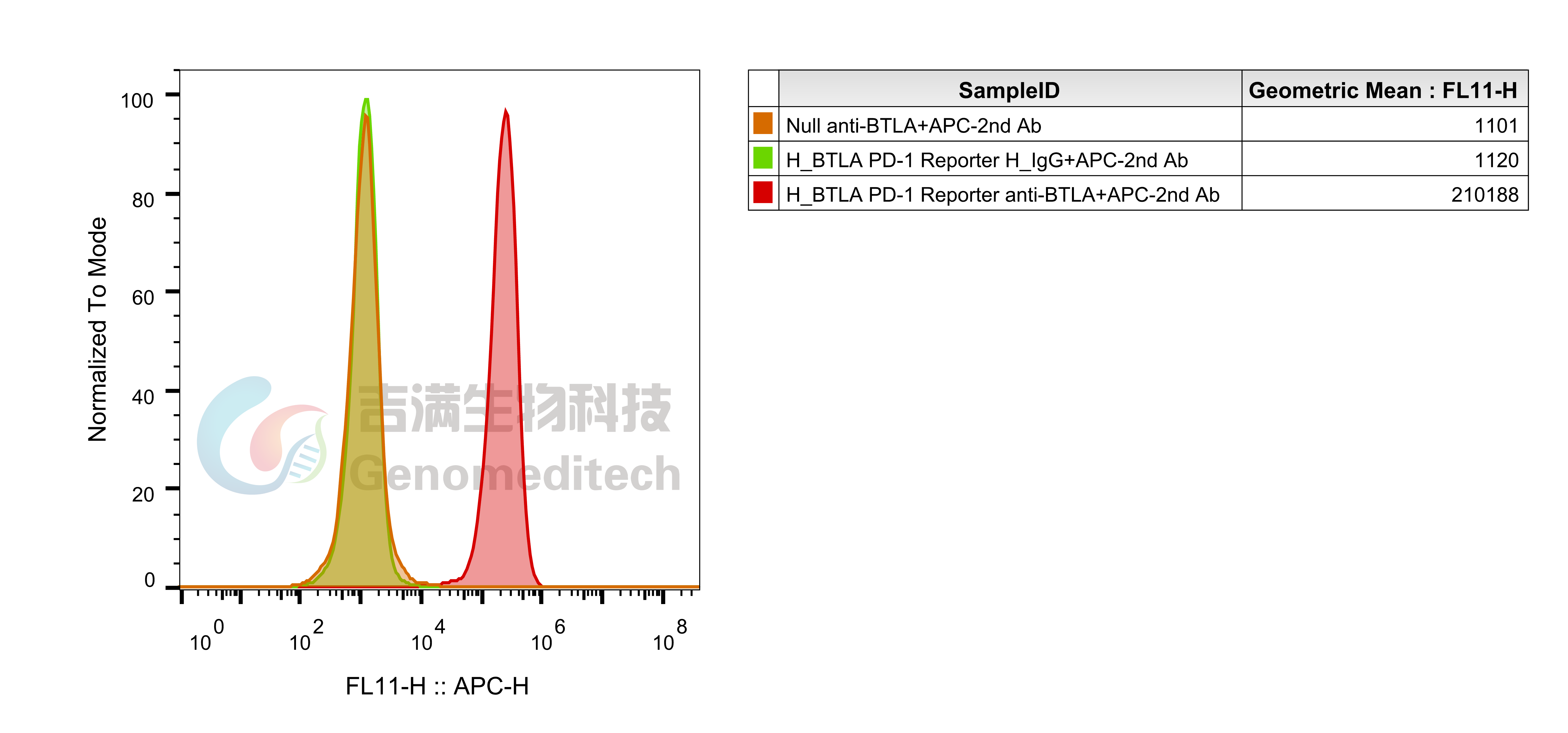
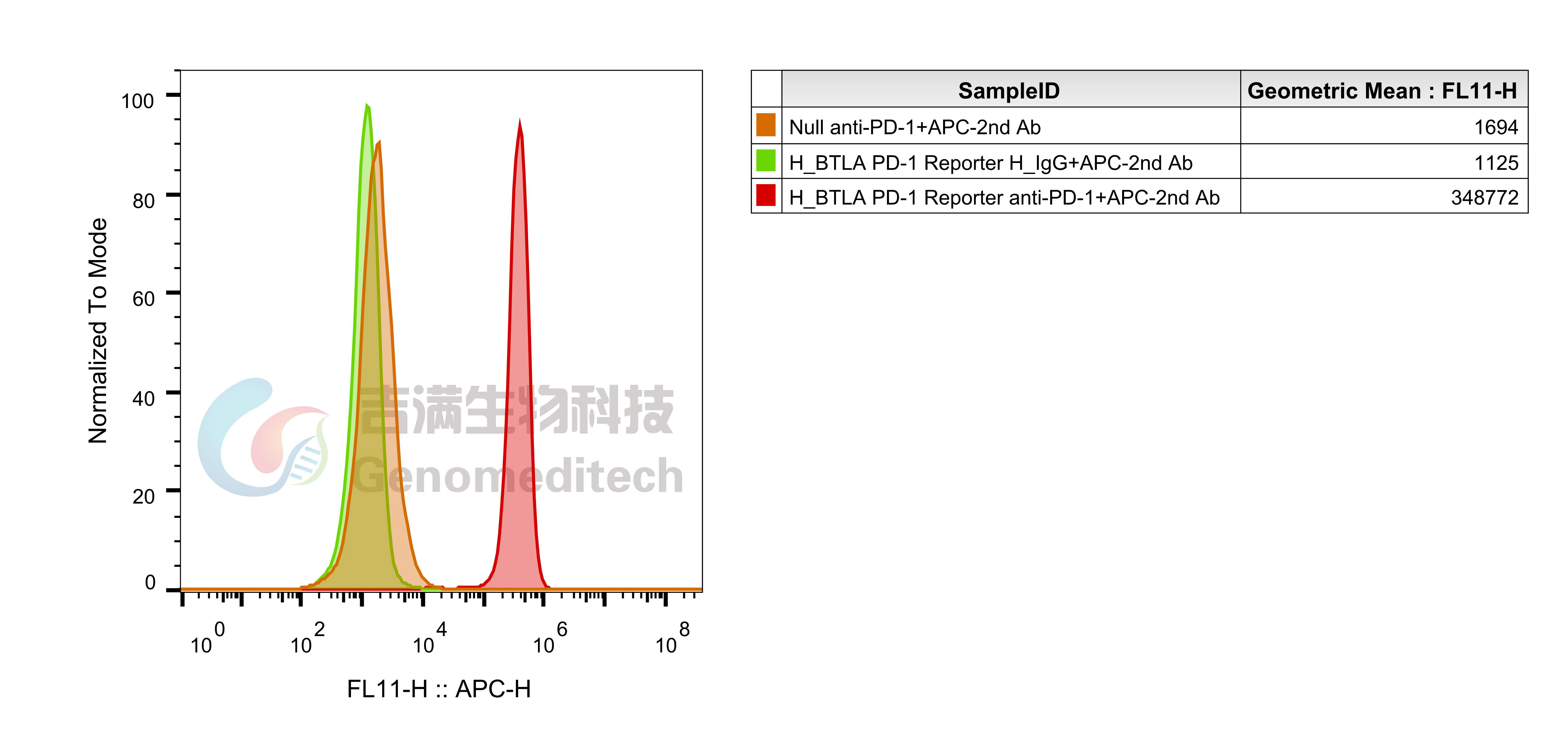
Cell Recovery
Recovery Medium: RPMI 1640+10% FBS+1% P.S
To insure the highest level of viability, thaw the vial and initiate the culture as soon as possible upon receipt. If upon arrival, continued storage of the frozen culture is necessary, it should be stored in liquid nitrogen vapor phase and not at -70°C. Storage at -70°C will result in loss of viability.
a) Thaw the vial by gentle agitation in a 37°C water bath. To reduce the possibility of contamination, keep the O-ring and cap out of the water. Thawing should be rapid (approximately 2 - 3 minutes).
b) Remove the vial from the water bath as soon as the contents are thawed, and decontaminate by dipping in or spraying with 70% ethanol. All of the operations from this point on should be carried out under strict aseptic conditions.
c) Transfer the vial contents to a centrifuge tube containing 5.0 mL complete culture medium. And spin at approximately 176 x g for 5 minutes. Discard supernatant.
d) Resuspend cell pellet with the recommended complete medium. And dispense the suspension into 1 - 2 T-25 culture flasks.
e) Incubate the culture at 37°C in a suitable incubator. A 5% CO₂ in air atmosphere is recommended if using the medium described on this product sheet.
Freezing Medium: 90% FBS+10% DMSO
a) Centrifuge at 176 x g for 3 minutes to collect cells.
b) Resuspend the cells in pre-cooled freezing medium and adjust the cell density to 5E6 cells/mL.
c) Aliquot 1 mL into each vial.
d) Place the vial in a controlled-rate freezing container and store at -80°C for at least 1 day, then transfer to liquid nitrogen as soon as possible.
Cell passage
Growth medium: RPMI 1640+10% FBS+1% P.S+3.5 μg/mL Blasticidin+400 μg/mL Bleomycin+0.75 μg/mL Puromycin
Approximately 48-72 hours after the initial thawing, the cells can be passaged for the first time. After this initial passage, the culture medium can be adjusted to growth medium supplemented with antibiotics. If cells are not passaged within 48 hours, it is recommended to add some fresh recovery medium and place the flask horizontally.
a) When the cell density reaches 1.5 - 2E6 cells/mL, subculture the cells. Do not allow the cell density to exceed 2E6 cells/mL.
b) It is recommended to use T-25 flasks for subculturing.
c) These cells are suspension cells, and it is recommended to use the "half-medium change" method to maintain optimal cell conditions during passaging.
d) During passaging, you can directly add fresh growth medium to the culture flask, gently pipette to resuspend the cells, and then transfer the cell suspension to a new T-25 flask for continued culture.
Subcultivation Ratio: Maintain cultures at a cell concentraion between 3E5 and 1E6 viable cells/mL.
Medium Renewal: Every 2 to 3 days
Notes
a) These cells are sensitive to density, so please ensure that the cell density is maintained within an appropriate range during culture and subculturing.
b) During the first passage, pay attention to the nutrient supply; if not subculturing, make sure to add fresh recovery medium every other day as needed.