Cat.NO:GM-27203AB
Product:Anti-H_CTLA-4 hIgG1 Antibody(Ipilimumab)
Cat.NO:GM-27203AB
Product:Anti-H_CTLA-4 hIgG1 Antibody(Ipilimumab)
GM-27203AB-10 10 μg
GM-27203AB-100 100 μg
GM-27203AB-1000 1mg
Species Reactivity Human; Cynomolgus
Clone Ipilimumab
Source/Isotype Monoclonal Human IgG1 /κ
Application Flow Cytometry; Bioassay
Specificity Detects CTLA-4
Gene CTLA-4
Other Names ALPS5, CD, CD152, CELIAC3, CTLA4, GRD4, GSE, IDDM12
Gene ID 1493(human); G7PL88-1(Cynomolgus)
Background CTLA-4 or CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed in regulatory T cells but only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation – a phenomenon which is particularly notable in cancers. It acts as an "off" switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. CTLA-4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed by activated T cells and transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. CTLA-4 is homologous to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein, CD28, and both molecules bind to CD80 and CD86, also called B7-1 and B7-2 respectively, on antigen-presenting cells. CTLA-4 binds CD80 and CD86 with greater affinity and avidity than CD28 thus enabling it to outcompete CD28 for its ligands. CTLA-4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. CTLA-4 is also found in regulatory T cells (Tregs) and contributes to their inhibitory function. T cell activation through the T cell receptor and CD28 leads to increased expression of CTLA-4.
Storage Store at 2-8℃ short term (1-2 weeks).Store at ≤ -20℃ long term. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw.
Formulation Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2.
Endotoxin < 1 EU/mg, determined by LAL gel clotting assay
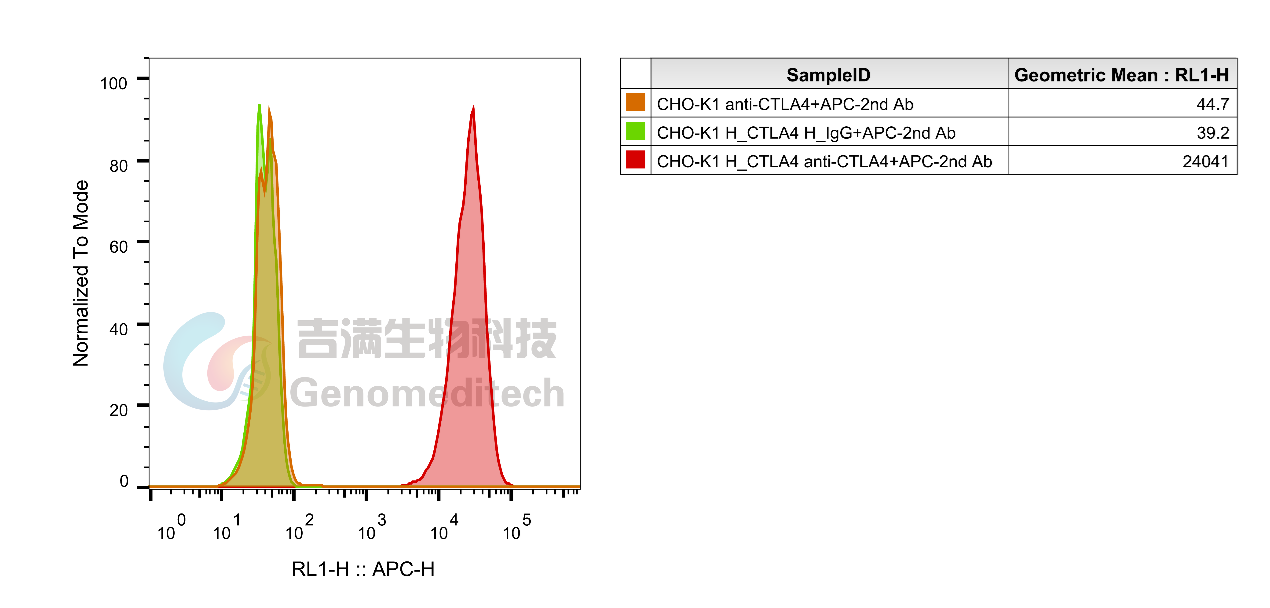
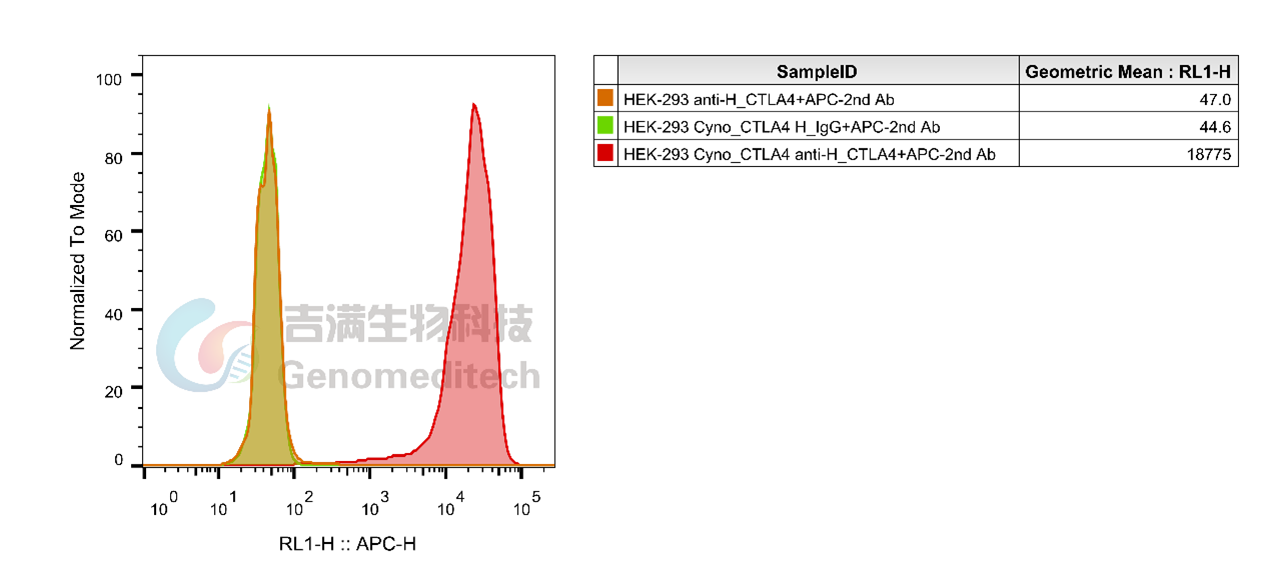



Cat.NO:GM-27203AB
Product:Anti-H_CTLA-4 hIgG1 Antibody(Ipilimumab)
GM-27203AB-10 10 μg
GM-27203AB-100 100 μg
GM-27203AB-1000 1mg
Species Reactivity Human; Cynomolgus
Clone Ipilimumab
Source/Isotype Monoclonal Human IgG1 /κ
Application Flow Cytometry; Bioassay
Specificity Detects CTLA-4
Gene CTLA-4
Other Names ALPS5, CD, CD152, CELIAC3, CTLA4, GRD4, GSE, IDDM12
Gene ID 1493(human); G7PL88-1(Cynomolgus)
Background CTLA-4 or CTLA4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4), also known as CD152 (cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed in regulatory T cells but only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation – a phenomenon which is particularly notable in cancers. It acts as an "off" switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. CTLA-4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed by activated T cells and transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. CTLA-4 is homologous to the T-cell co-stimulatory protein, CD28, and both molecules bind to CD80 and CD86, also called B7-1 and B7-2 respectively, on antigen-presenting cells. CTLA-4 binds CD80 and CD86 with greater affinity and avidity than CD28 thus enabling it to outcompete CD28 for its ligands. CTLA-4 transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells, whereas CD28 transmits a stimulatory signal. CTLA-4 is also found in regulatory T cells (Tregs) and contributes to their inhibitory function. T cell activation through the T cell receptor and CD28 leads to increased expression of CTLA-4.
Storage Store at 2-8℃ short term (1-2 weeks).Store at ≤ -20℃ long term. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw.
Formulation Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2.
Endotoxin < 1 EU/mg, determined by LAL gel clotting assay




