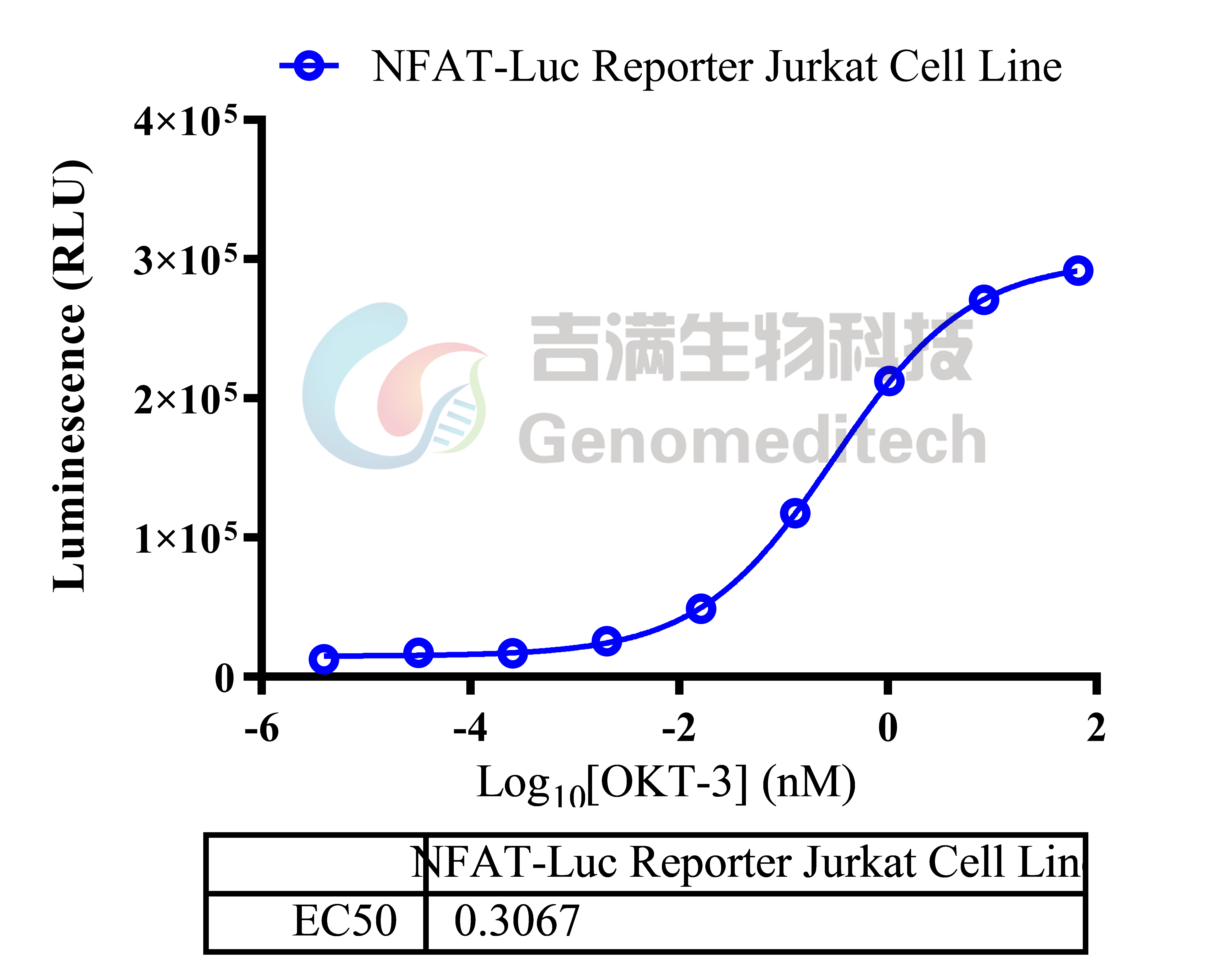
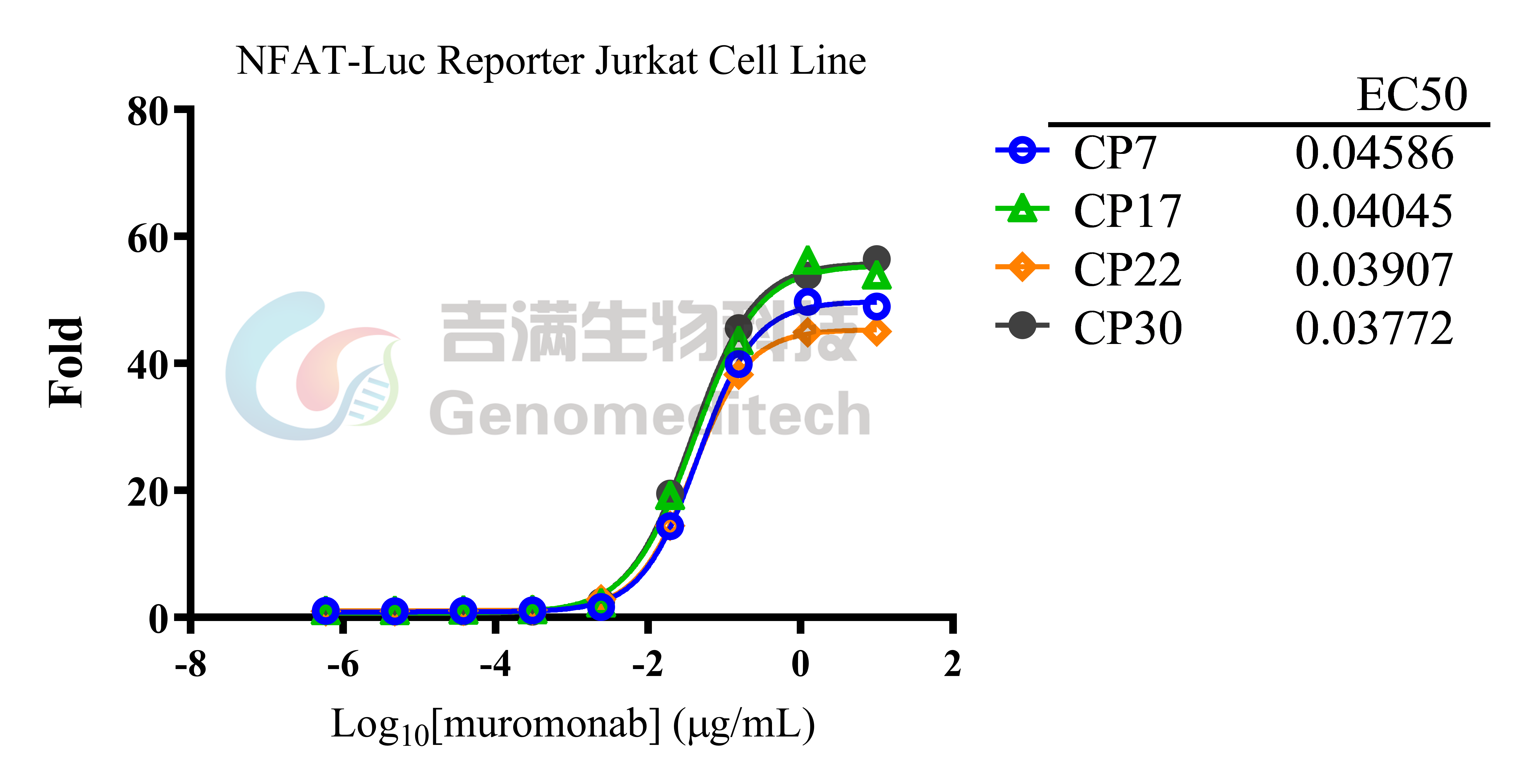
| Cat. No: GM-C01459 Product: NFAT-Luc Reporter Jurkat Cell Line NFAT (Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells) is a crucial transcription factor for immune cell function, especially T cell activation. The NFAT family includes NFATc1, NFATc2, NFATc3, and NFATc4, which are involved in calcium signaling and cytokine gene expression. NFAT is activated by rising calcium levels, leading to its dephosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus, where it binds to DNA to regulate gene transcription. The NFAT signaling pathway is activated by T cell receptors (TCR) and other surface receptors. When TCR binds to an antigen, intracellular calcium levels increase, activating phospholipase C (PLC) and producing diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). IP3 triggers calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum, activating calmodulin and calcium-dependent enzymes (like CaMK), which dephosphorylate NFAT, allowing its entry into the nucleus. NFAT interacts with other transcription factors (e.g., AP-1) to regulate immune-related gene expression, promoting T cell proliferation, differentiation, and cytokine production. NFAT-Luc Reporter Jurkat Cell Line is a clonal stable Jurkat cell line constructed using lentiviral technology that expresses a NFAT-inducible luciferase reporter gene. When the upstream signaling pathways are activated, the NFAT activates the expression of luciferase. The luciferase readout represents the activation level of the signaling pathway and can thus be used for evaluating the in vitro effects of related drugs. | 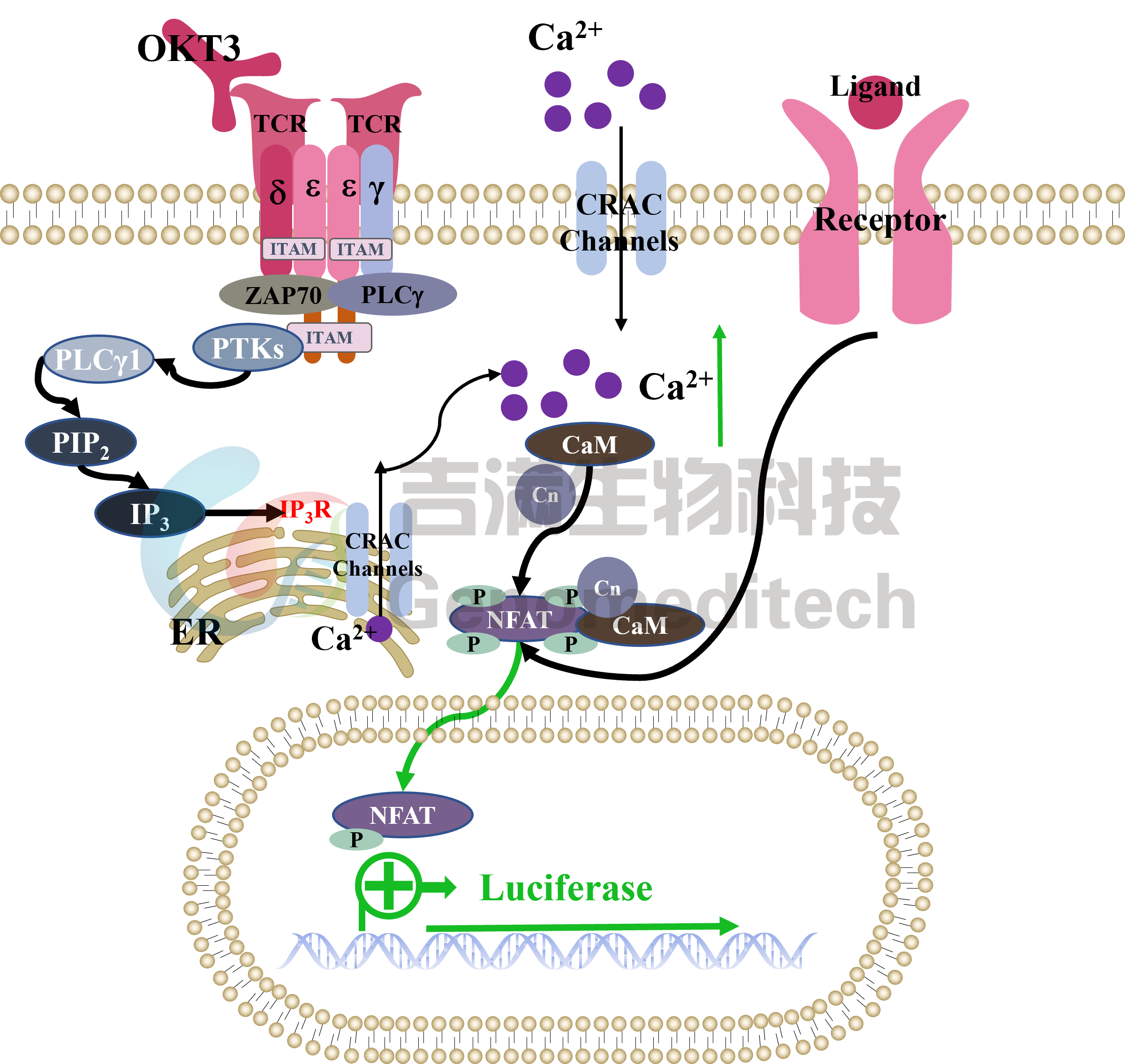 |