Cat. No:GM-86853MAB
Product:Anti-PDL1 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Adebio)
Cat. No:GM-86853MAB
Product:Anti-PDL1 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Adebio)
GM-86853MAB-1mg / 1 mg
GM-86853MAB-5mg / 5 mg
GM-86853MAB-25mg / 25 mg
GM-86853MAB-50mg / 50 mg
GM-86853MAB-100mg / 100 mg
Expression System CHO
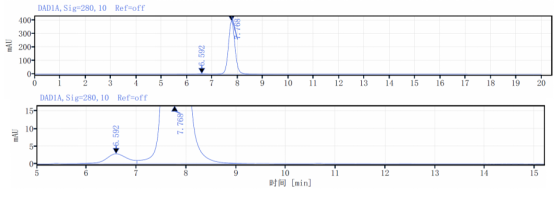
Aggregation < 5% as determined by SEC-HPLC
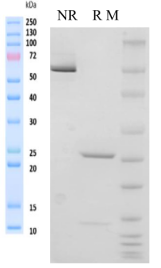
Purity > 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
Endotoxin < 1 EU/mg, determined by LAL gel clotting assay
Sterility 0.2 μm Filtered
Target PDL1
Clone Adebrelimab
Alternative Names B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, CD274, hPD-L1
Source/Isotype Human IgG4(S228P,L234A/L235A),Kappa
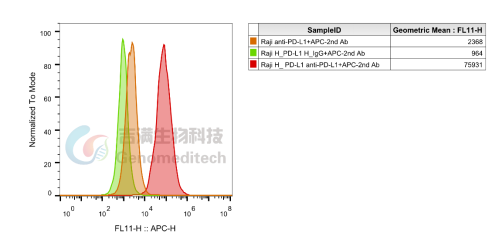
Application Flow cytometry
Description The programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1, PDCD1, CD279) is a member of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors that regulate T cell activation and immune responses. The PD-1 protein contains an extracellular Ig V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail that includes an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). PD-1 is activated by the cell surface ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Upon activation, PD-1 ITIM and ITSM phosphorylation leads to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which suppress TCR signaling. In addition to activated T-cells, PD-1 is expressed in activated B-cells and monocytes, although its function in these cell types has not been fully characterized. The PD-1 pathway plays an important role in immune tolerance; however, research studies show that cancer cells often adopt this pathway to escape immune surveillance. Consequently, blockade of PD-1 and its ligands is proving to be a soundThe programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1, PDCD1, CD279) is a member of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors that regulate T cell activation and immune responses. The PD-1 protein contains an extracellular Ig V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail that includes an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). PD-1 is activated by the cell surface ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Upon activation, PD-1 ITIM and ITSM phosphorylation leads to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which suppress TCR signaling. In addition to activated T-cells, PD-1 is expressed in activated B-cells and monocytes, although its function in these cell types has not been fully characterized. The PD-1 pathway plays an important role in immune tolerance; however, research studies show that cancer cells often adopt this pathway to escape immune surveillance. Consequently, blockade of PD-1 and its ligands is proving to be a sound strategy for neoplastic intervention.
Formulation phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.4.


Cat. No:GM-86853MAB
Product:Anti-PDL1 hIgG4 Reference Antibody (Adebio)
GM-86853MAB-1mg / 1 mg
GM-86853MAB-5mg / 5 mg
GM-86853MAB-25mg / 25 mg
GM-86853MAB-50mg / 50 mg
GM-86853MAB-100mg / 100 mg
Expression System CHO
Aggregation < 5% as determined by SEC-HPLC
Purity > 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
Endotoxin < 1 EU/mg, determined by LAL gel clotting assay
Sterility 0.2 μm Filtered
Target PDL1
Clone Adebrelimab
Alternative Names B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, CD274, hPD-L1
Source/Isotype Human IgG4(S228P,L234A/L235A),Kappa
Application Flow cytometry
Description The programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1, PDCD1, CD279) is a member of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors that regulate T cell activation and immune responses. The PD-1 protein contains an extracellular Ig V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail that includes an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). PD-1 is activated by the cell surface ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Upon activation, PD-1 ITIM and ITSM phosphorylation leads to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which suppress TCR signaling. In addition to activated T-cells, PD-1 is expressed in activated B-cells and monocytes, although its function in these cell types has not been fully characterized. The PD-1 pathway plays an important role in immune tolerance; however, research studies show that cancer cells often adopt this pathway to escape immune surveillance. Consequently, blockade of PD-1 and its ligands is proving to be a soundThe programmed cell death 1 protein (PD-1, PDCD1, CD279) is a member of the CD28 family of immunoreceptors that regulate T cell activation and immune responses. The PD-1 protein contains an extracellular Ig V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail that includes an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM). PD-1 is activated by the cell surface ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Upon activation, PD-1 ITIM and ITSM phosphorylation leads to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2, which suppress TCR signaling. In addition to activated T-cells, PD-1 is expressed in activated B-cells and monocytes, although its function in these cell types has not been fully characterized. The PD-1 pathway plays an important role in immune tolerance; however, research studies show that cancer cells often adopt this pathway to escape immune surveillance. Consequently, blockade of PD-1 and its ligands is proving to be a sound strategy for neoplastic intervention.
Formulation phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.4.




