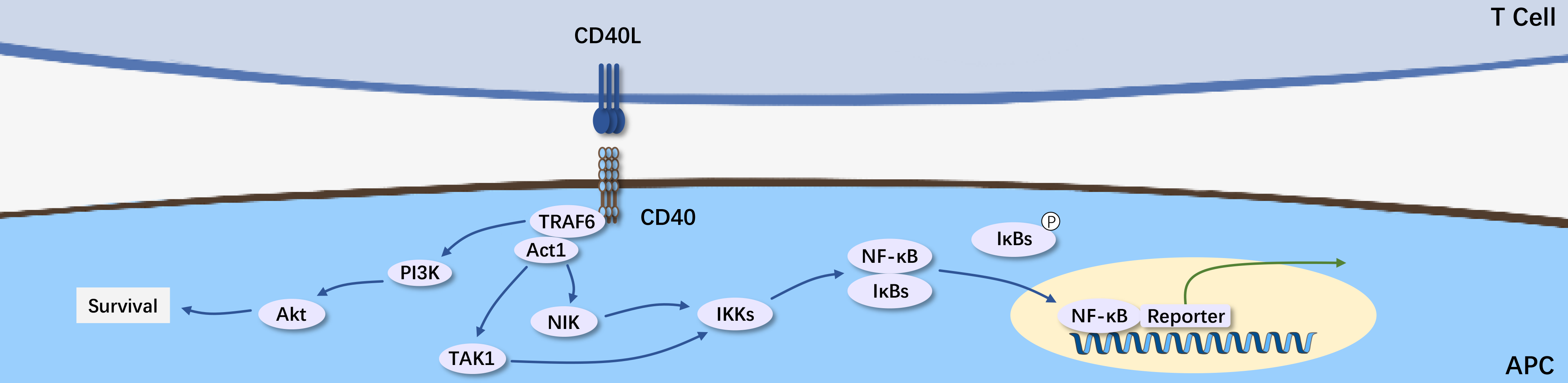
CD40, also known as TNFRSF5, is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily protein, expressed in various cell types including immune cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and some tumor cells. Its ligand CD154 (CD40L) is mainly expressed on activated T cells. Research has shown that CD40-CD40L plays a crucial role in the immune response, particularly in the function of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), which is essential for adaptive immune responses.
Currently, drug development targeting CD40 can be categorized into activation (agonists) or inhibition (antagonists) to enhance immune activity in cancer environments or suppress the immune system in autoimmune disease environments. However, as a monotherapy, CD40 antibodies only exhibit moderate activity, with tumor objective response rates below 20%, especially in "cold tumors" with insufficient immune responses or tumors where immune cells are not highly infiltrated, leading many CD40-related projects to stagnate.
Given the relatively low efficacy of CD40 monotherapy, exploring more potential combination therapies is a feasible solution. Therefore, selecting appropriate in vitro cell models for functional validation becomes particularly crucial.