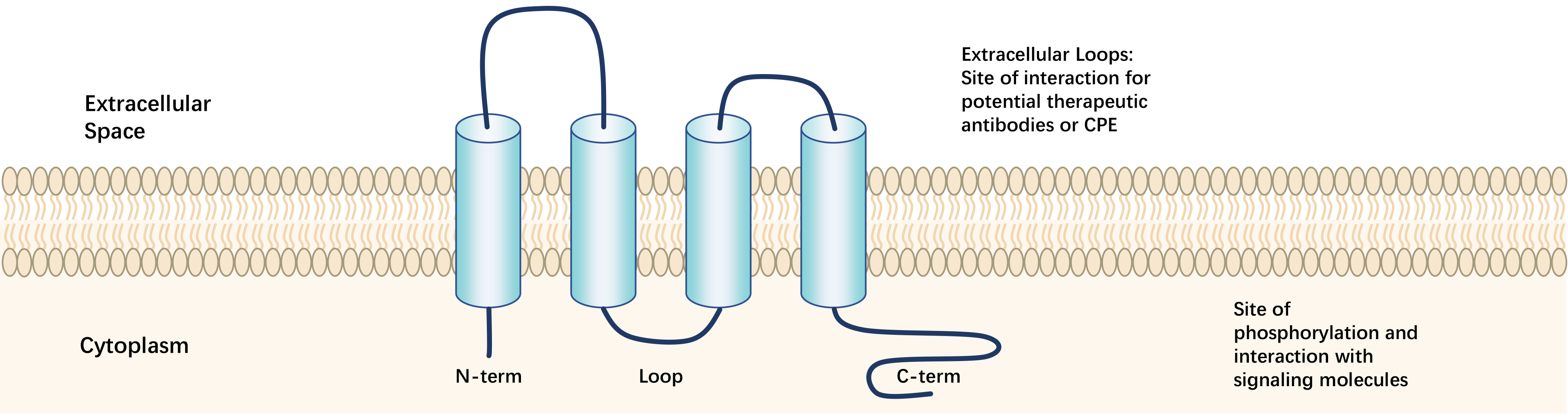
The Claudin protein family is encoded by the CLDN gene family, consisting of proteins with a relative molecular weight of 25,000-27,000. In mammals, it comprises 27 members with high sequence homology, subject to regulation at both the translation and transcription levels. The secondary structure of Claudin proteins is mainly composed of helical bundles and β-sheets, with four tightly wound helical bundles forming four transmembrane domains (TM1-TM4) embedded within the cell membrane.
Claudin proteins are primarily expressed in epithelial cells of the body, exhibiting significant tissue specificity. Different Claudin proteins show varying distributions in different organs. The tissue-specificity of Claudin proteins results in diverse impacts on tumors, where expressions like Claudin 5 and Claudin 9 are downregulated in cervical cancer while Claudin 8 is upregulated. Claudin proteins play crucial roles in various common cancers such as breast, liver, lung, colorectal, and gastric cancers.
The gastric mucosal barrier, formed by the cell membrane at the top of gastric epithelial cells and tight connections between adjacent cells, is the main mechanism protecting the gastric mucosa. As an important protein related to gastric epithelial cell connections, abnormal expression of Claudin may lead to damage to the gastric mucosal barrier, resulting in diseases like gastric cancer. Moreover, dysfunctional tight connections due to abnormal expression of Claudin proteins can also promote tumor growth and metastasis.